Design of an angle measurement system based on interferometric fringe imaging and its off-axis measurement accuracy
-
摘要:
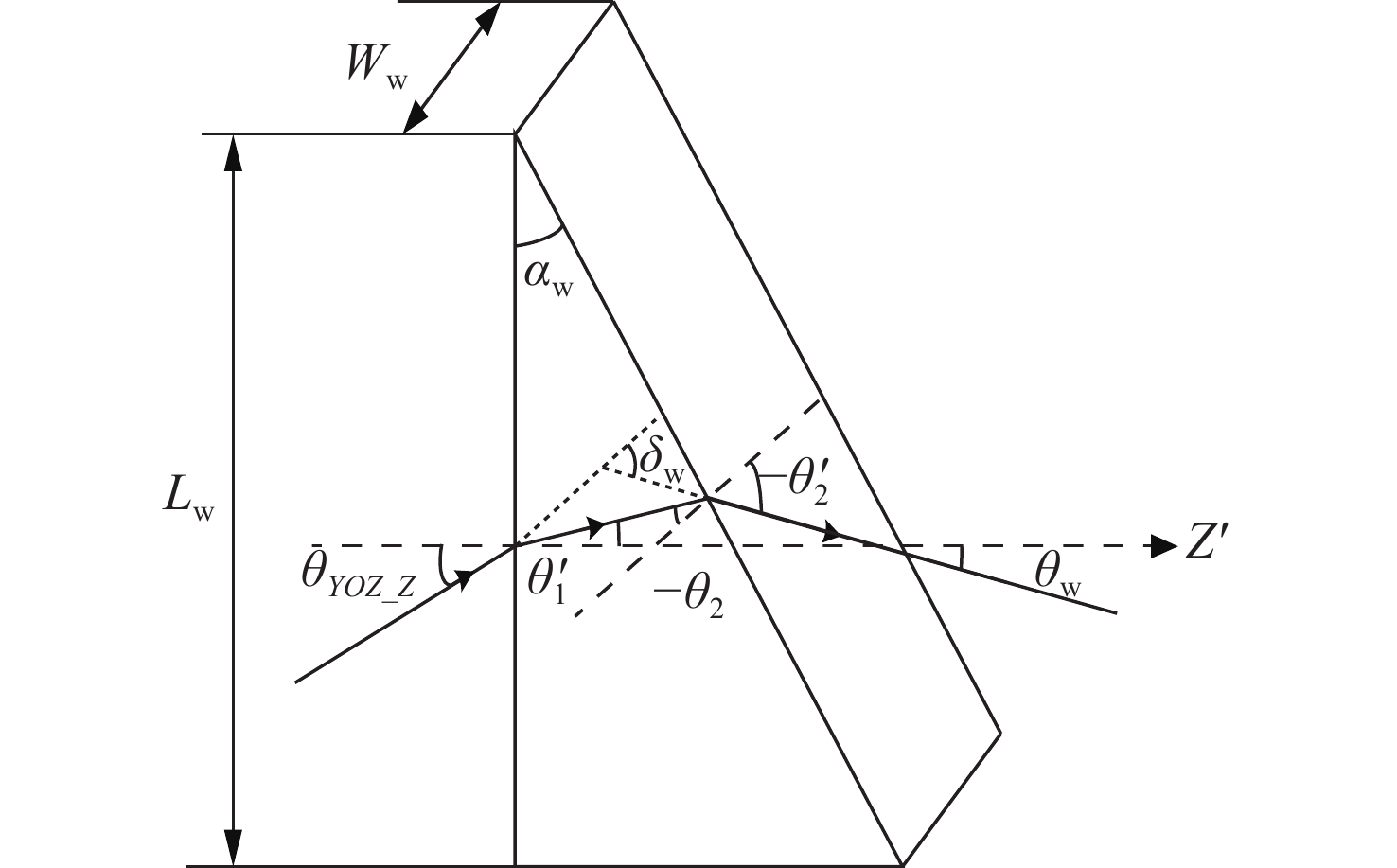
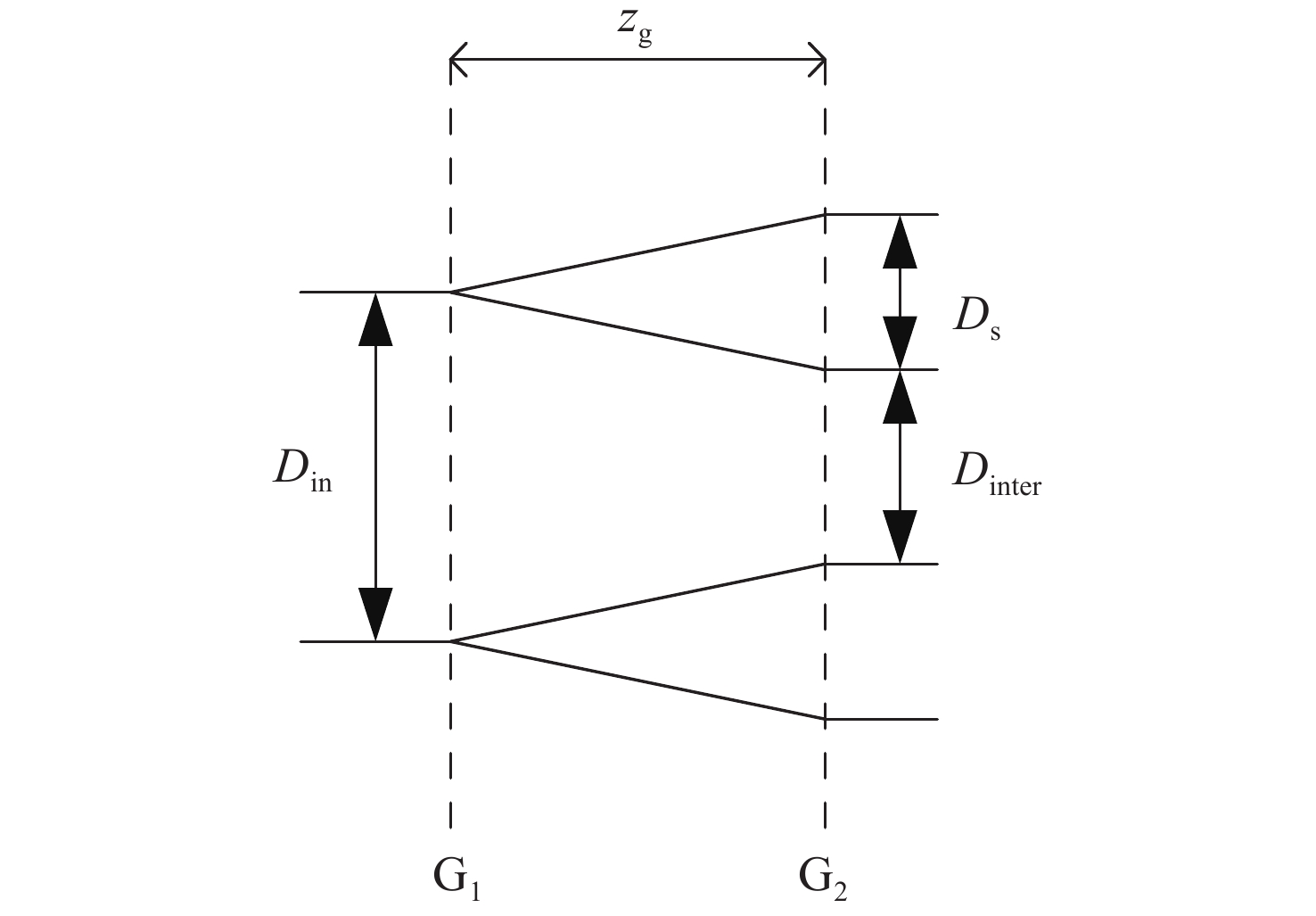
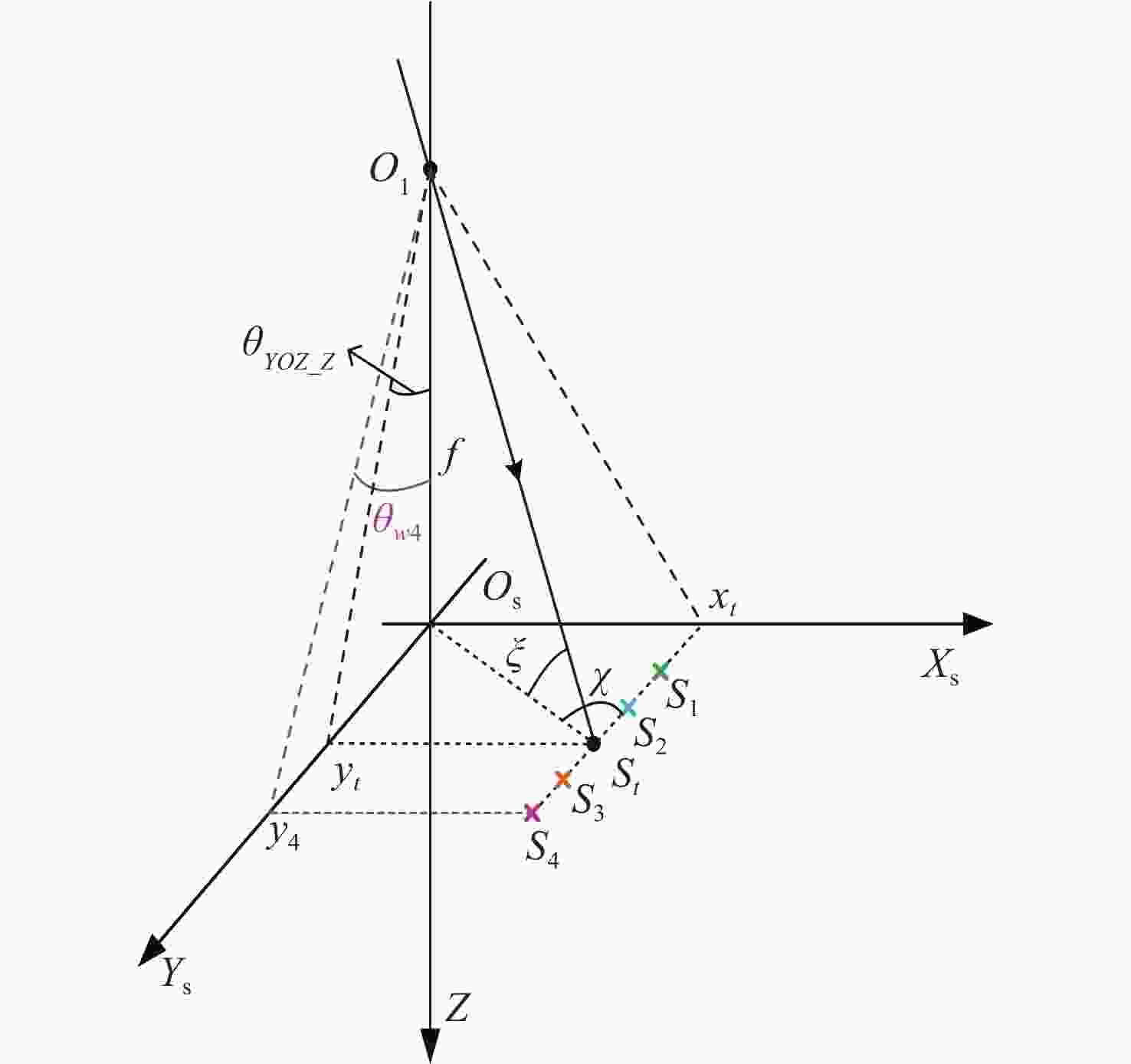
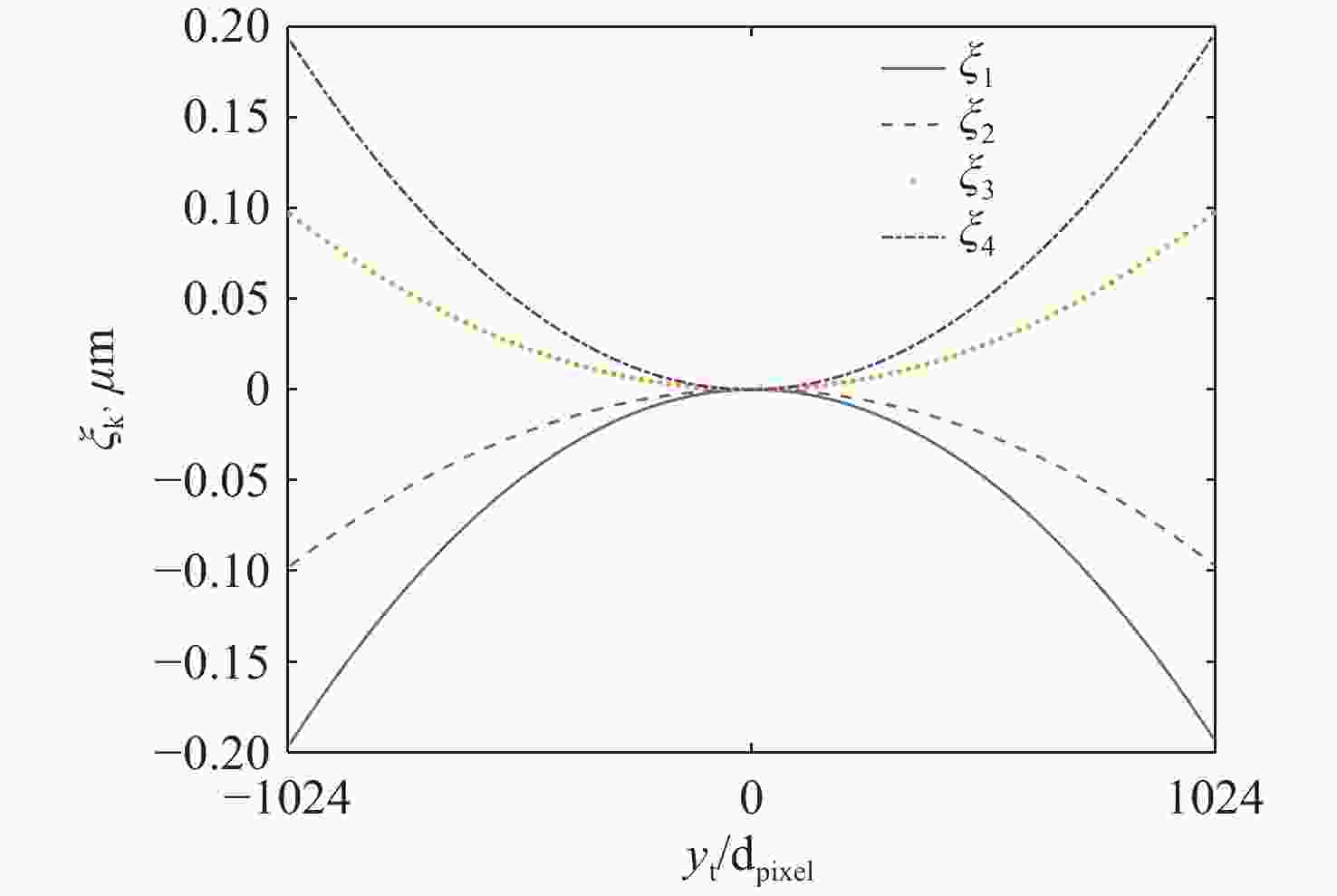
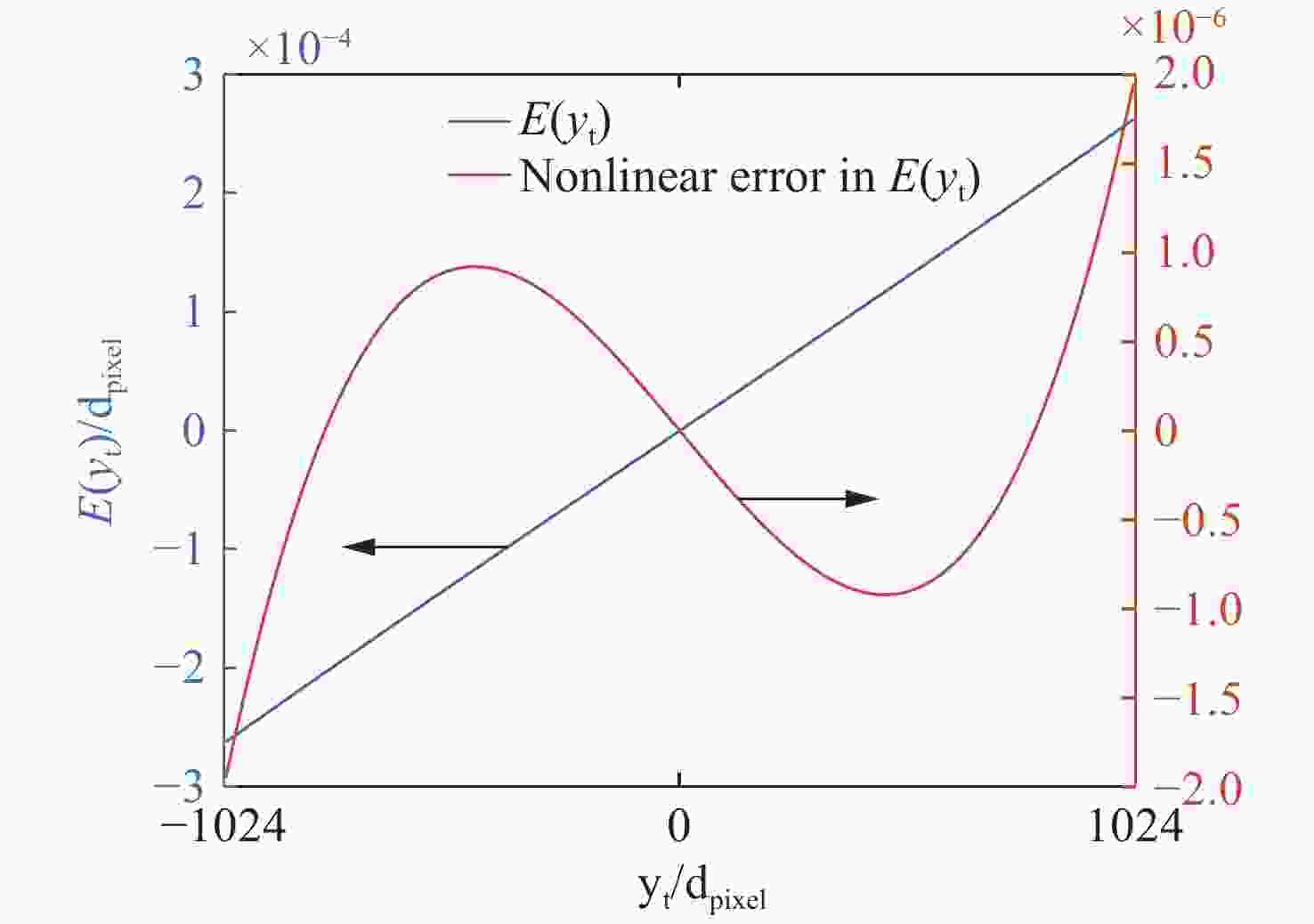
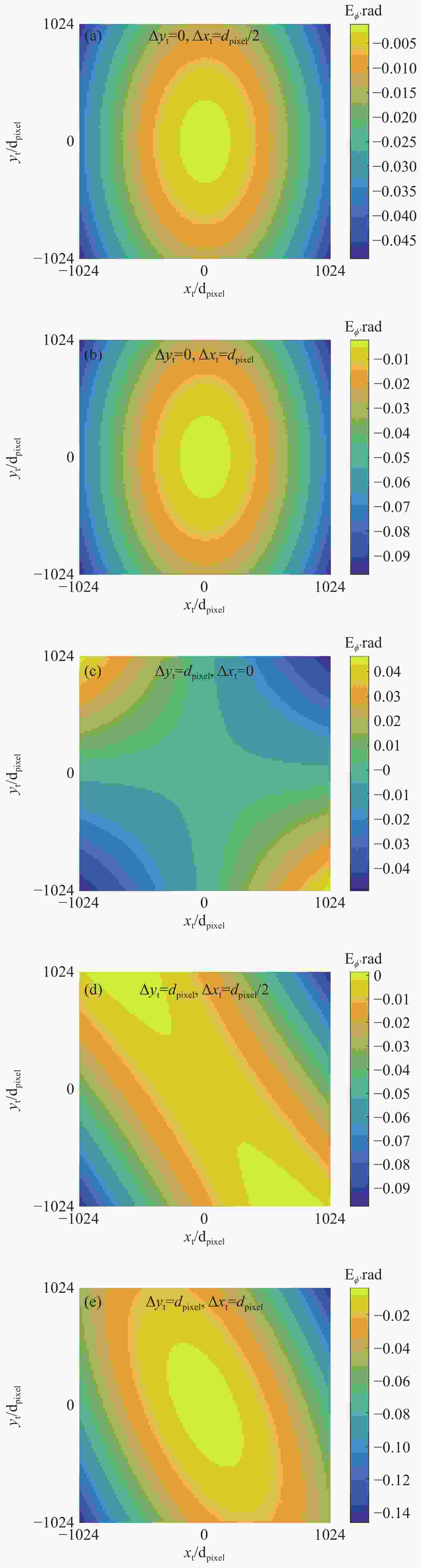
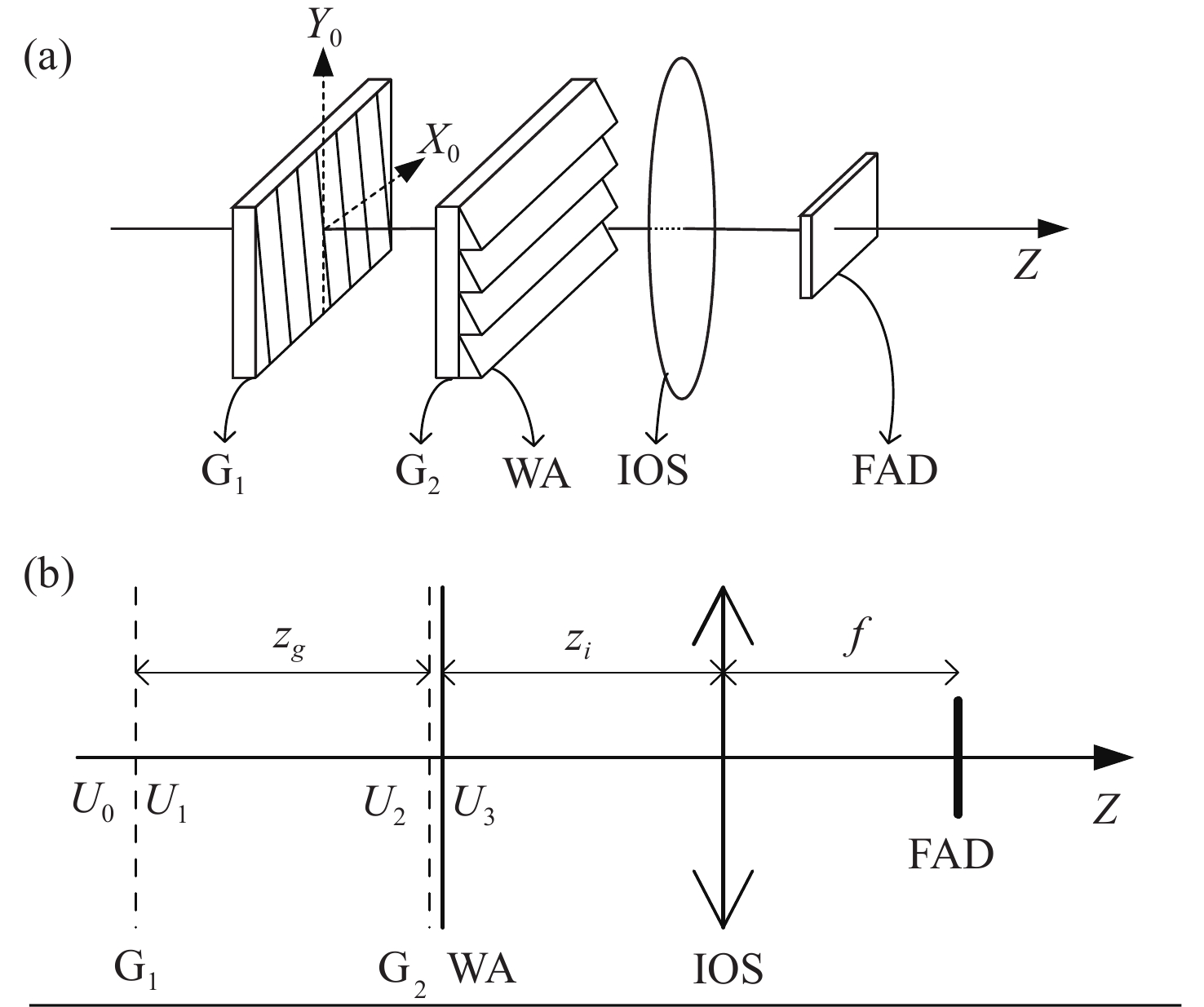
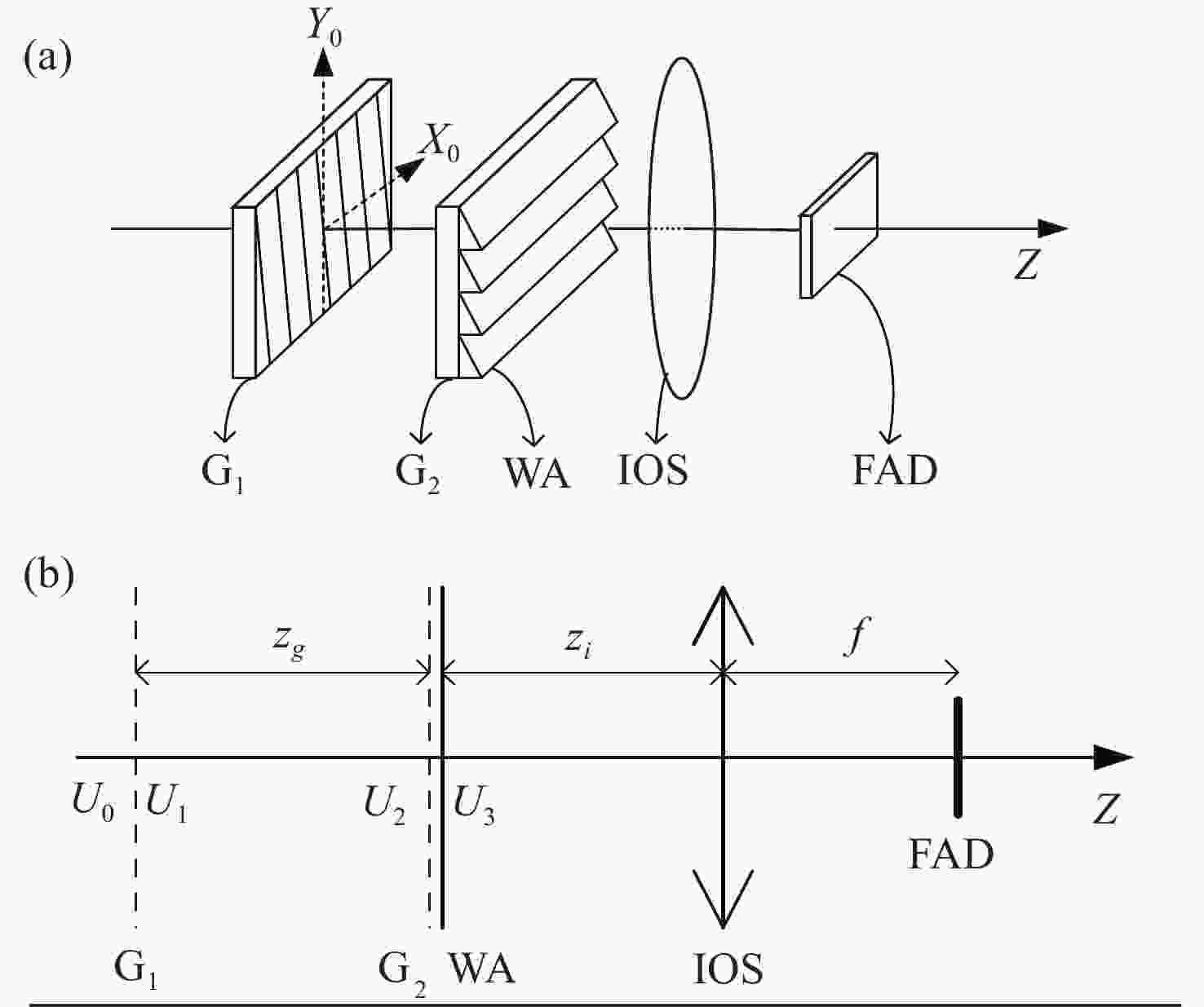
基于干涉条纹成像的测角系统测量精度随着测量范围的增大而下降,单纯提高精定位的细分倍数并不能提高测量精度。针对这一问题,本文围绕非成像系统的参数设计方法及大测量范围下的精度变化情况展开研究。建立了双光栅干涉系统及光楔阵列波前分割的数学模型,给出了近轴条件下非成像光学系统的参数设计方法。设计了一台一维高精度光学测角系统,并对该系统在整个测角范围内的测量误差进行了分析和计算。结果显示:利用本文提出的数学模型和方法,所设计的测角系统在[−5°,5°]的测量范围内,近轴区的测角分辨率为0.02″。随着测量范围的增大,干涉条纹相位非线性变化引起的精定位误差成为系统测角误差的主要来源,最大测量角度下精密轴的测量误差为0.42″。上述结果表明采用本文提出的模型和参数设计方法,可以设计出具有较高测角精度的光学测角系统。
Abstract:The accuracy of an angle measurement system based on interferometric fringe imaging decreases as the measurement range increases. Merely increasing the subdivision factor of precise positioning cannot improve the accuracy of the measurement. In this case, this paper primarily focuses on the parameter design method in non-imaging optical systems and accuracy changes under a wide measurement range. The mathematical models for the dual grating interference system and the wavefront segmentation of the optical wedge array were established, and a parameter design method for non-imaging optical systems under paraxial conditions was proposed. A one-dimensional high-precision angle measurement system was designed, and the measurement error of the system within the measurement range was analyzed and calculated. The results show that the designed angle measurement system achieves a resolution of 0.02" in the paraxial region with a measurement range of [−5°,5°] based on the mathematical model and method proposed in this paper. As the measurement range expands, the precision positioning errors resulting from nonlinear changes in the phase of interference fringes become the primary source of measurement errors. At the maximum measurement angle, the accuracy of the precision axis reduces to 0.42". The above results demonstrate that the proposed model and parameter design method can be employed to design an optical angle measurement system with high accuracy.
-
-
[1] 浦昭邦, 陶卫, 张琢. 角度测量的光学方法[J]. 光学技术,2002,28(2):168-171. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2002.02.011PU ZH B, TAO W, ZHANG ZH. Angle measurement with optical methods[J]. Optical Technique, 2002, 28(2): 168-171. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2002.02.011 [2] 张博, 段锦, 景文博. 基于CCD的光学测角精度检测方法[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2010,33(4):55-57.ZHANG B, DUAN J, JING W B. CCD-based optical detection precision of angle measurement[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 33(4): 55-57. (in Chinese). [3] 戴嘉伟, 王海朋, 陈瀑, 等. 多光谱数据融合分析技术的研究和应用进展[J]. 分析化学,2022,50(6):839-849.DAI J W, WANG H M, CHEN P, et al. Progress and application of multi-spectral data fusion methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(6): 839-849. [4] 李自力, 徐兴冉, 湛江浩, 等. 先进光刻材料[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(6):859-870.LI Z L, XU X R, ZHAN J H, et al. Advanced materials for lithography[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(6): 859-870. [5] 陈士恒, 王林涛, 龚明明, 等. 高灵敏度便携式铀分析仪的研制[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(9):1414-1422.CHEN SH H, WANG L T, GONG M M, et al. Development of portable trace uranium analyzer with high sensitivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(9): 1414-1422. [6] 程军杰, 曹智, 杨灿然, 等. 便携式远程激光诱导击穿光谱系统及其定量分析性能[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(9):1447-1452.CHENG J J, CAO ZH, YANG C R, et al. Quantitative analysis with a portable remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(9): 1447-1452. [7] 刘旭, 李杨可欣, 杜黎, 等. 水凝胶的制备及仿生设计在能源领域应用的研究进展[J]. 应用化学, 2022, 39(1): 35-54.LIU X, LI Y K X, DU L, et al. Bio-inspired hydrogels: synthesis, bionic design and applications in the field of energy storage and conversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry,2022,39(1):35-54. [8] 王磊, 宦克为, 刘小溪, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的近红外光谱全流程分析模型研究[J]. 分析化学,2022,50(12):1918-1926.WANG L, HUAN K W, LIU X X, et al. Full-range analysis model of near infrared spectroscopy based on convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(12): 1918-1926. [9] 陈志斌, 肖文健, 马东玺, 等. 大尺寸空间角测量技术进展及其分析[J]. 应用光学,2016,37(3):407-414. doi: 10.5768/JAO201637.0303002CHEN ZH B, XIAO W J, MA D X, et al. Technical progress and analysis on large-scale spatial angle measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Optics, 2016, 37(3): 407-414. (in Chinese). doi: 10.5768/JAO201637.0303002 [10] HUTCHIN R A. Interferometric tracking device: US, 8045178[P]. 2011-10-25. [11] Optical Physics Company. Nary Profiles in Success Article, https://www.opci.com/products/star-tracker/[EB/OL]. 2024. [12] DU J, BAI J, HUANG X, et al. High-precision attitude angle measuring system based on Talbot interferometry[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10462: 104623L. [13] DU J, BAI J, WANG L, et al. Optical design and accuracy analysis of interferometric star tracker[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10815: 1081504. [14] 杜娟, 白剑, 黄潇, 等. 基于二维光栅的双轴干涉星敏感器装置: 中国, 207600470U[P]. 2017-08-28.DU J, BAI J, HUANG X, et al. Star sensor device is interfered to biax based on two -dimensional grating: CN, 207600470U[P]. 2017-08-28. (in Chinese). [15] 张淑芬. 基于衍射光栅的高精度干涉星敏感器研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021.ZHANG SH F. Research on high accuracy interferometric star tracker based on diffraction grating[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021. (in Chinese). [16] 董磊, 阮宇翔, 王建立, 等. 基于计算干涉测量的远距离目标高精度角度测量技术研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(18):1811016.DONG L, RUAN Y X, WANG J L, et al. Progress in high accurate angle measurement technology of long-distance target based on computational interferometry[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(18): 1811016. (in Chinese). [17] 张淑芬, 姜珊, 董磊, 等. 基于衍射光栅的高精度干涉星敏感器的理论分析[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1368-1377. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0051ZHANG SH F, JIANG SH, DONG L, et al. High accuracy interferometric star tracker based on diffraction grating[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1368-1377. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0051 [18] 阮宇翔, 董磊. 干涉星敏感器测角精度影响因素的研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1433-1441. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0232RUAN Y X, DONG L. Influencing factors of angle measurement accuracy of an interferometer star tracker[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1433-1441. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0232 [19] SCHREIBER H, SCHWIDER J. Lateral shearing interferometer based on two Ronchi phase gratings in series[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(22): 5321-5324. doi: 10.1364/AO.36.005321 [20] 吕乃光. 傅里叶光学[M]. 3版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2016.LV N G. Fourier Optics[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2016. (in Chinese). [21] SMITH W J. Modern Optical Engineering[M]. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008. [22] 李杰, 唐锋, 王向朝, 等. 光栅横向剪切干涉仪及其系统误差分析[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(5):0508006. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0508006LI J, TANG F, WANG X ZH, et al. System errors analysis of grating lateral shearing interferometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(5): 0508006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0508006 -





 下载:
下载: