-
摘要:
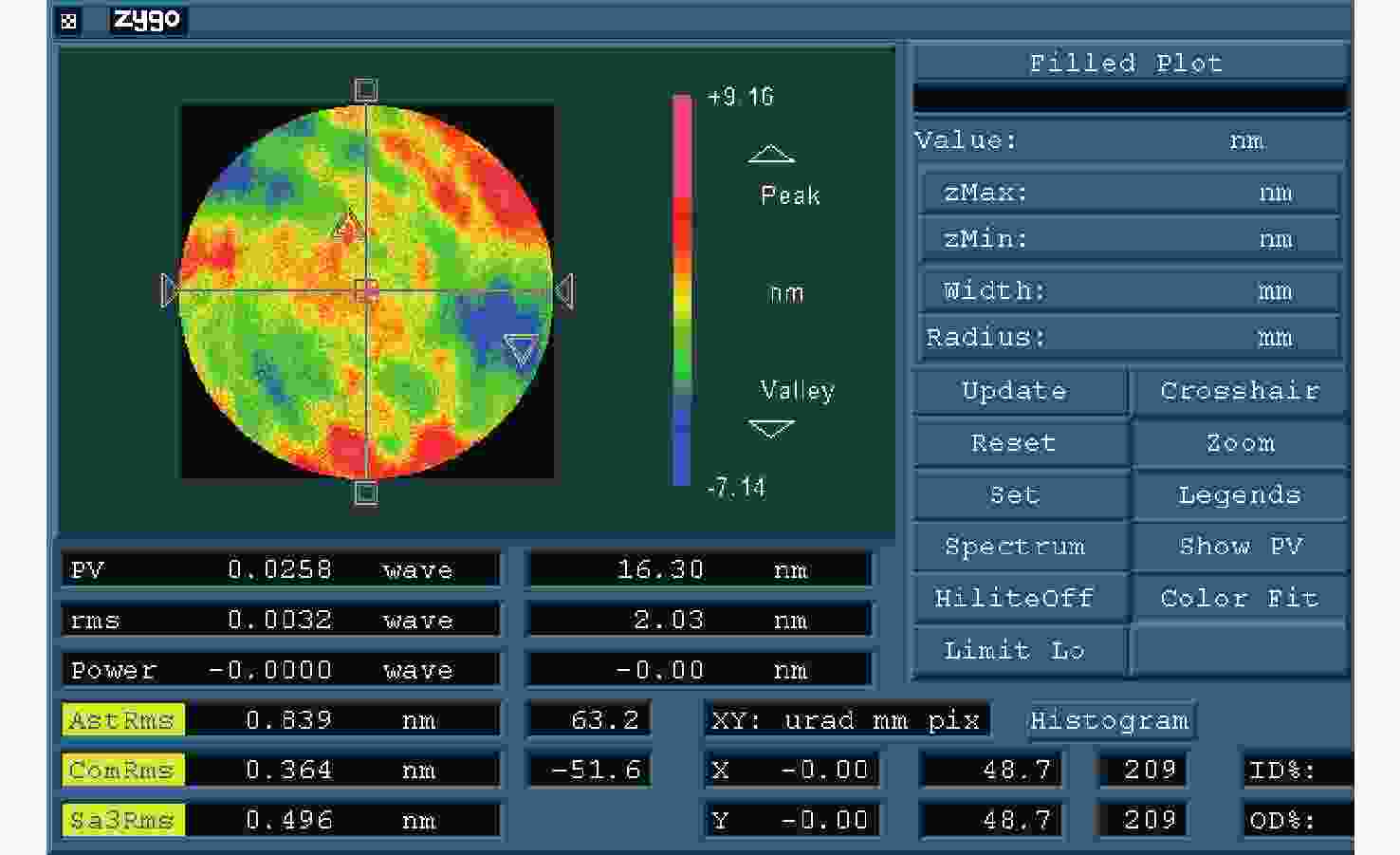
为了解决同轴高次非球面的高精度面形检测问题,本文提出了一种基于CGH的同轴高次非球面零位补偿检测设计方法。利用所提方法,可以实现同轴非球面补偿设计中各衍射级次的有效分离,可实现对于待测镜面的零位补偿设计。结合工程实例,本文对一口径为260 mm的同轴高次非球面反射镜实现了零位补偿检测设计。从CGH设计结果可以看出,基于本文检测设计方法,其理论设计检测残差(RMS值)可以达到0 nm。此外,还完成了对于该同轴高次非球面反射镜的实际检测。针对检测过程中的误差源进行了误差分析,以验证本方法的可靠性与精度。
Abstract:In order to solve problems involved in high-precision surface map testing of coaxial high-order aspherical surfaces, this paper proposes a null compensation testing method based on CGH. Based on this method, the separation of the diffraction order in the coaxial aspherical compensation design can be effectively realized, and the null compensation design of the mirror to be measured can also be realized. Combined with engineering examples, this paper realizes a null compensation testing design for a coaxial high-order aspherical mirror with a 260 mm aperture. The CGH design results show that the theoretical design testing residual (RMS value) can reach 0 nm based on the designed method. The practical testing of the coaxial high-order aspherical mirror is also completed. To further analyze the testing results, error analysis is carried out on the error source in the testing process, to verify the reliability and accuracy of the method.
-
表 1 待测高次非球面镜基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of the high-order aspherical mirror
参数项 参数数值 D/mm 260 r −4.62×102 k 1.192×10−1 A4 2.936×10−11 A6 2.875×10−15 表 2 检测光路基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of the detection optical path
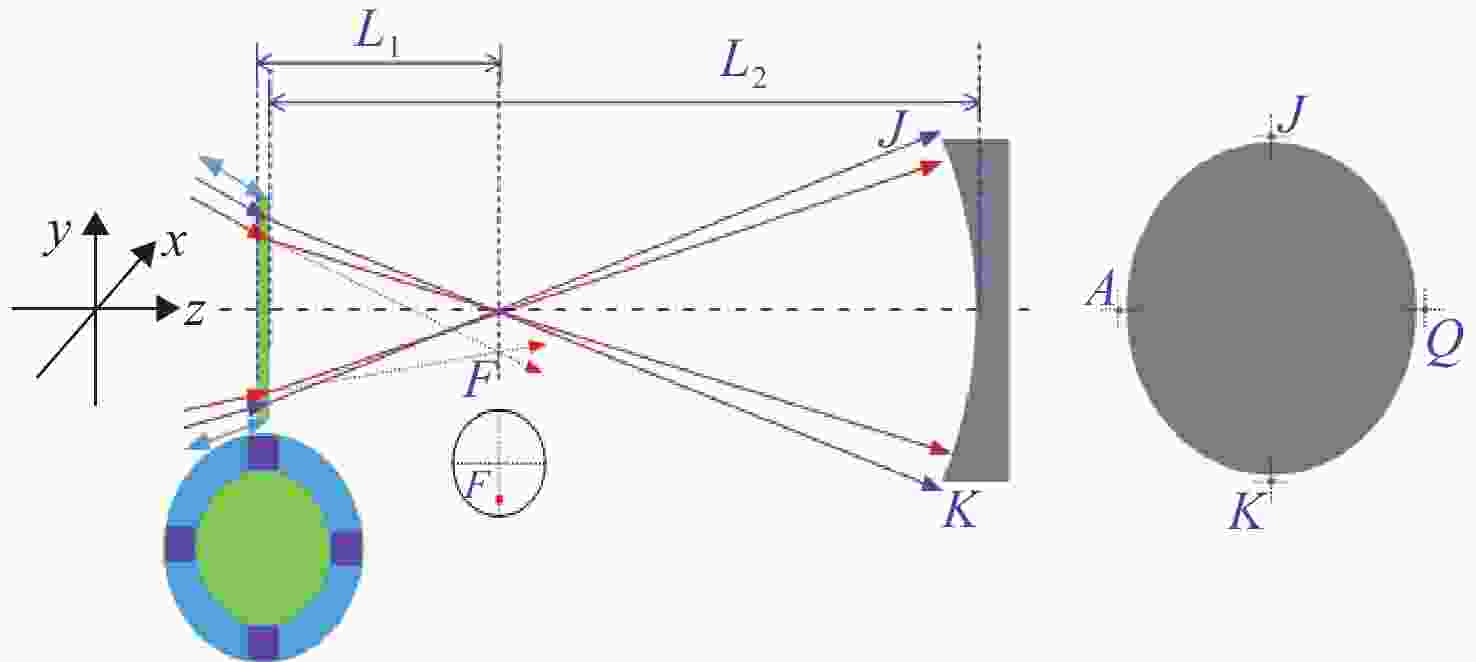
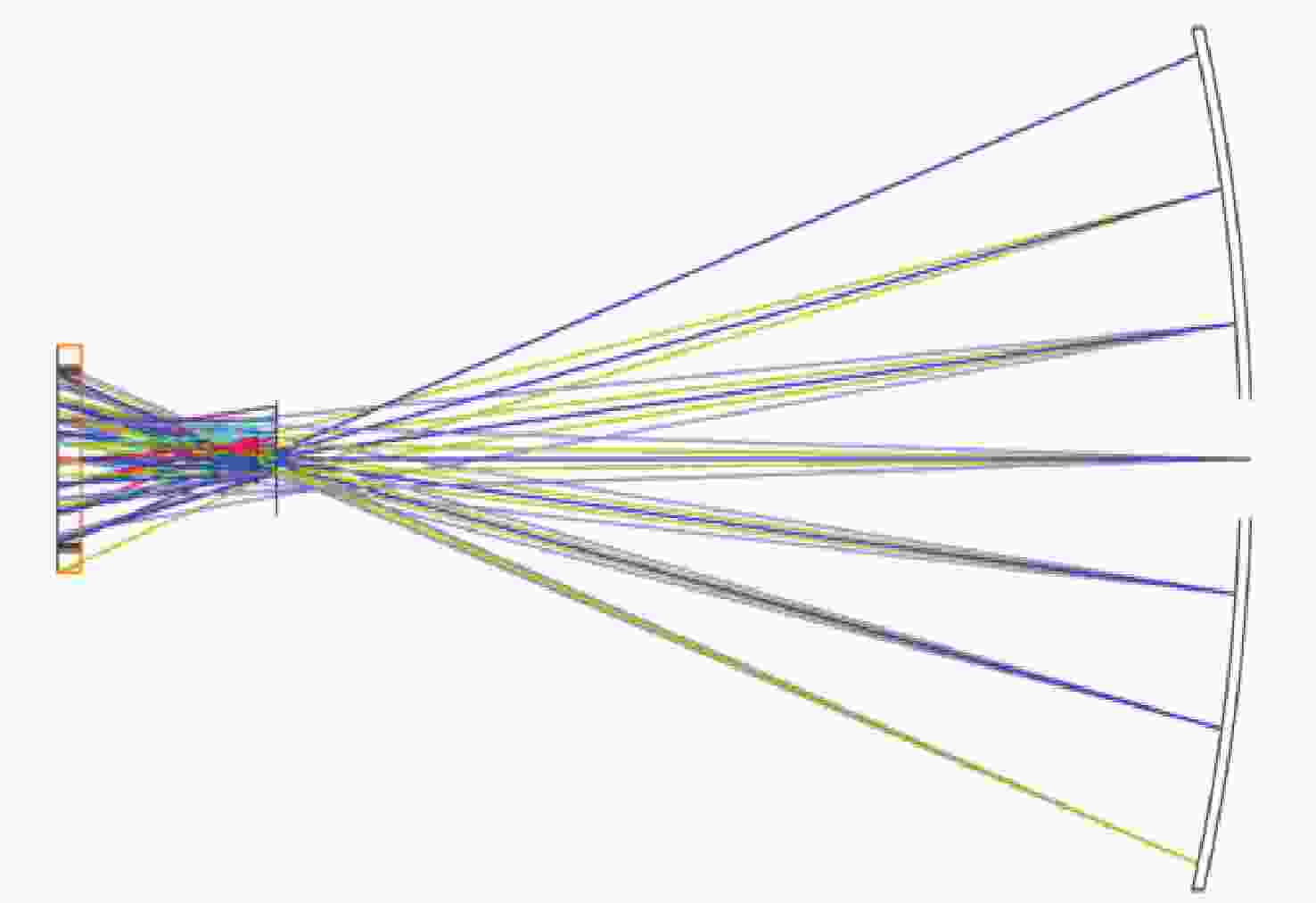
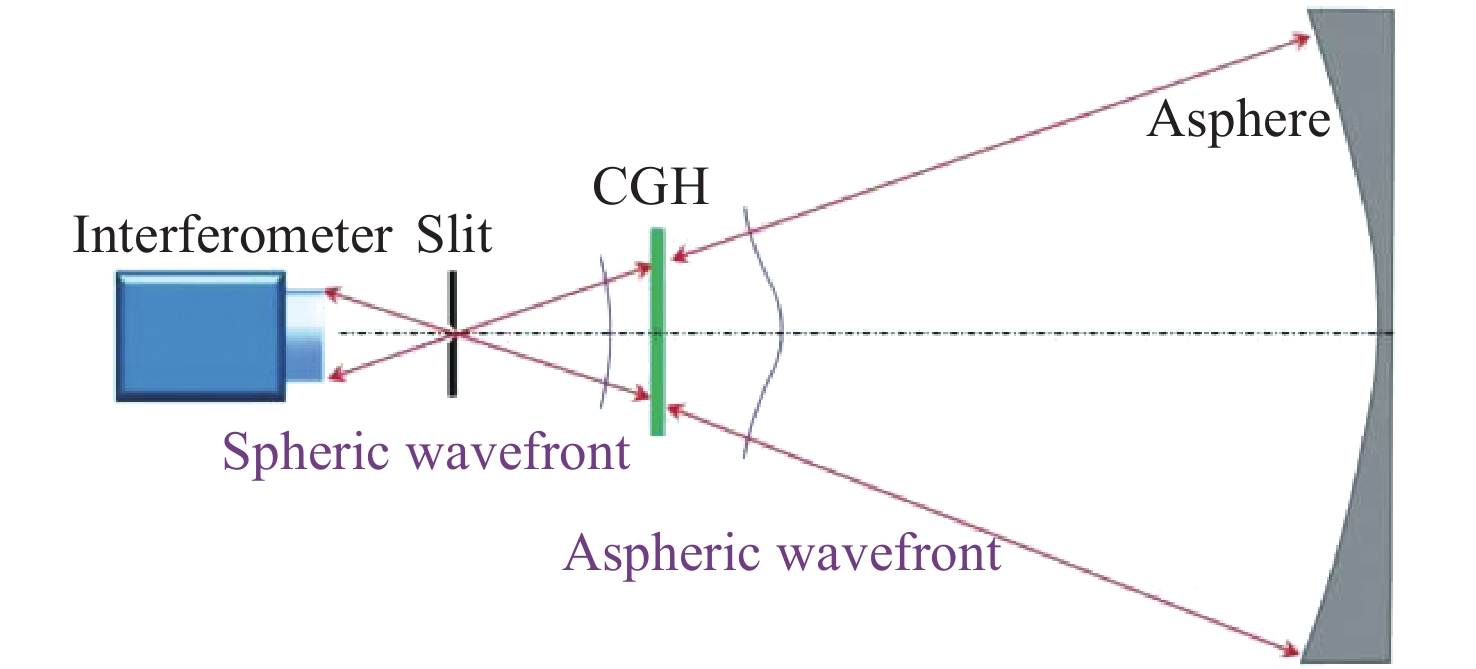
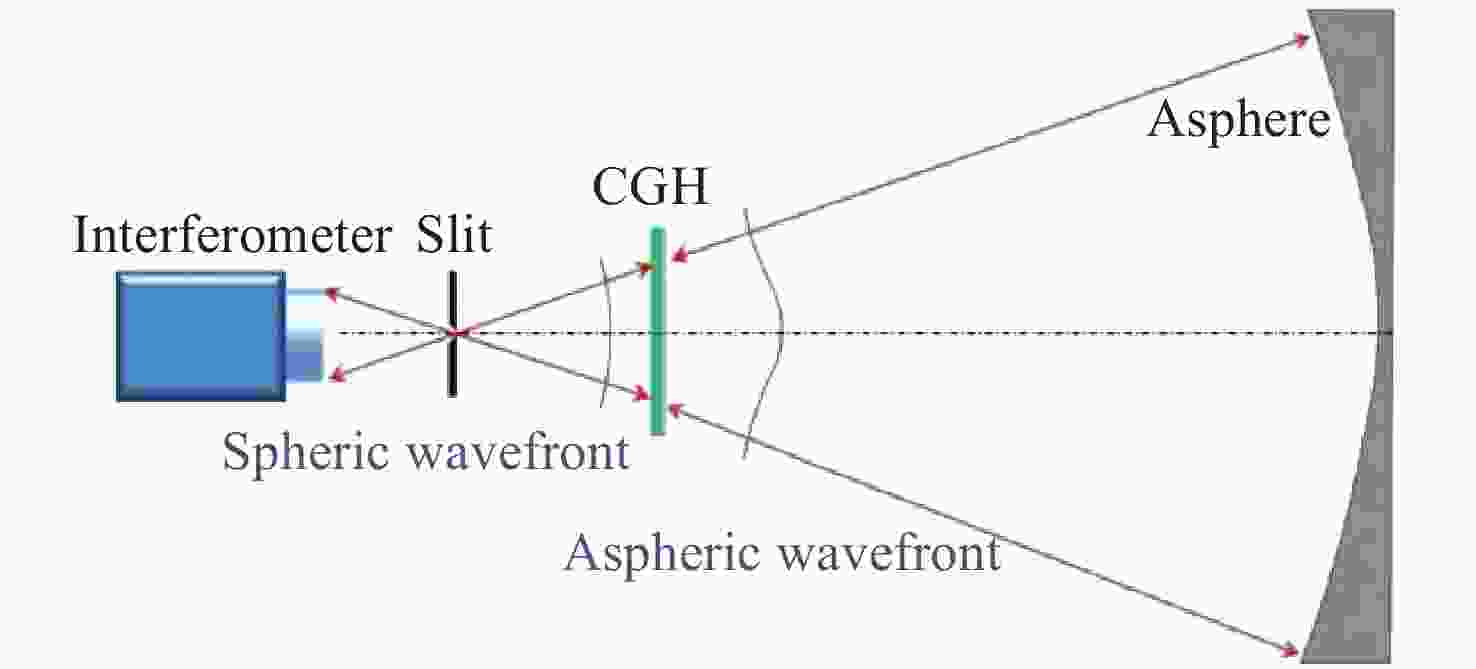
参数 数值 CGH基板 直径为100 mm; 厚度为15.07 mm;
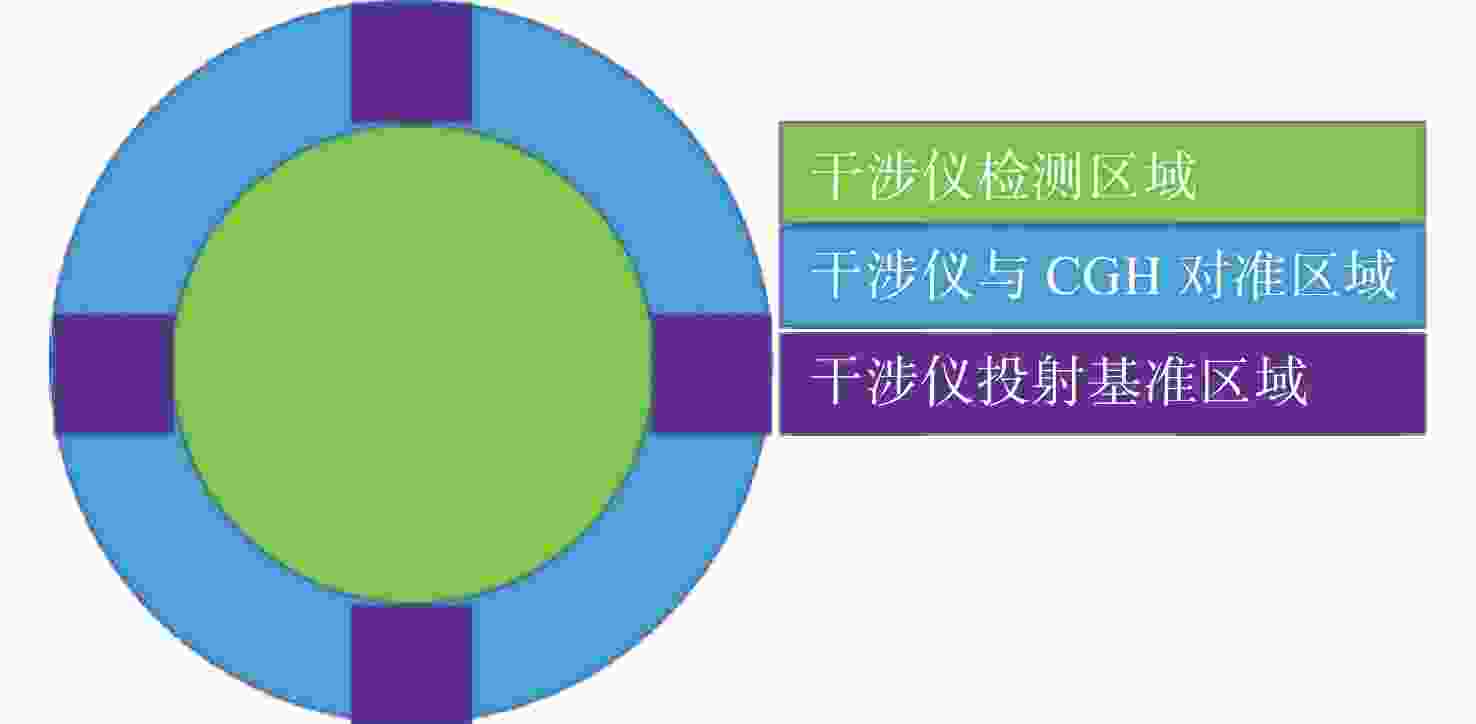
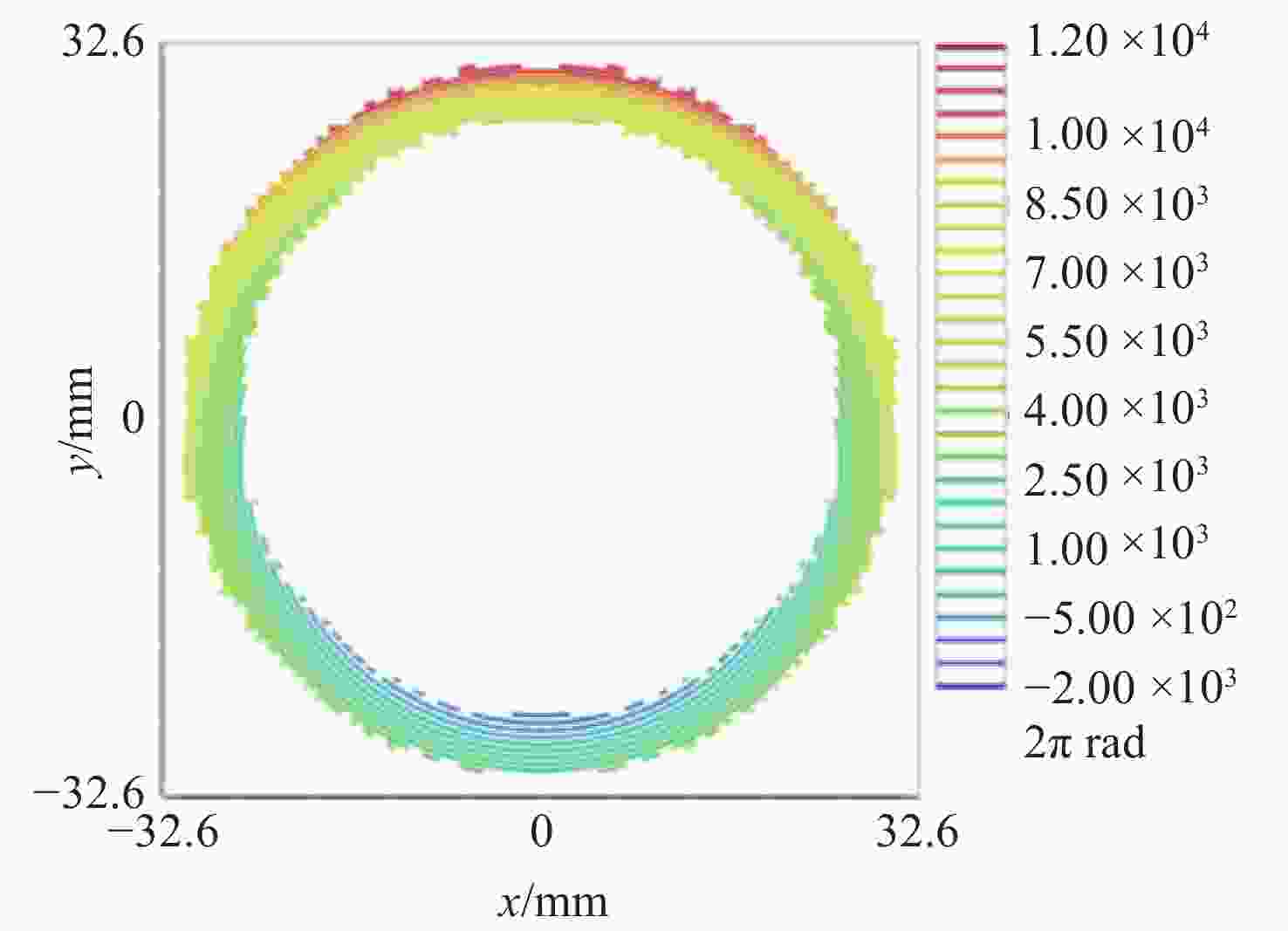
距离L1= 93.76; L2= 496 mm干涉仪焦点坐标 F(0, −4),单位mm 光阑参数 距离CGH后表面76.5 mm;直径1 mm 辅助对准区域(蓝色) 辅助CGH和干涉仪之间对准;辅助CGH和
平面镜直接对准;衍射级次5级基准投射区域(紫色) 在被检面处投射参考光斑;衍射级次1级 所投射4个光斑坐标 J(0, 132.14), Q(132.14, 0), K(0, -132.14),
A(−132.14, 0),单位mm表 3 主区域光学设计结果
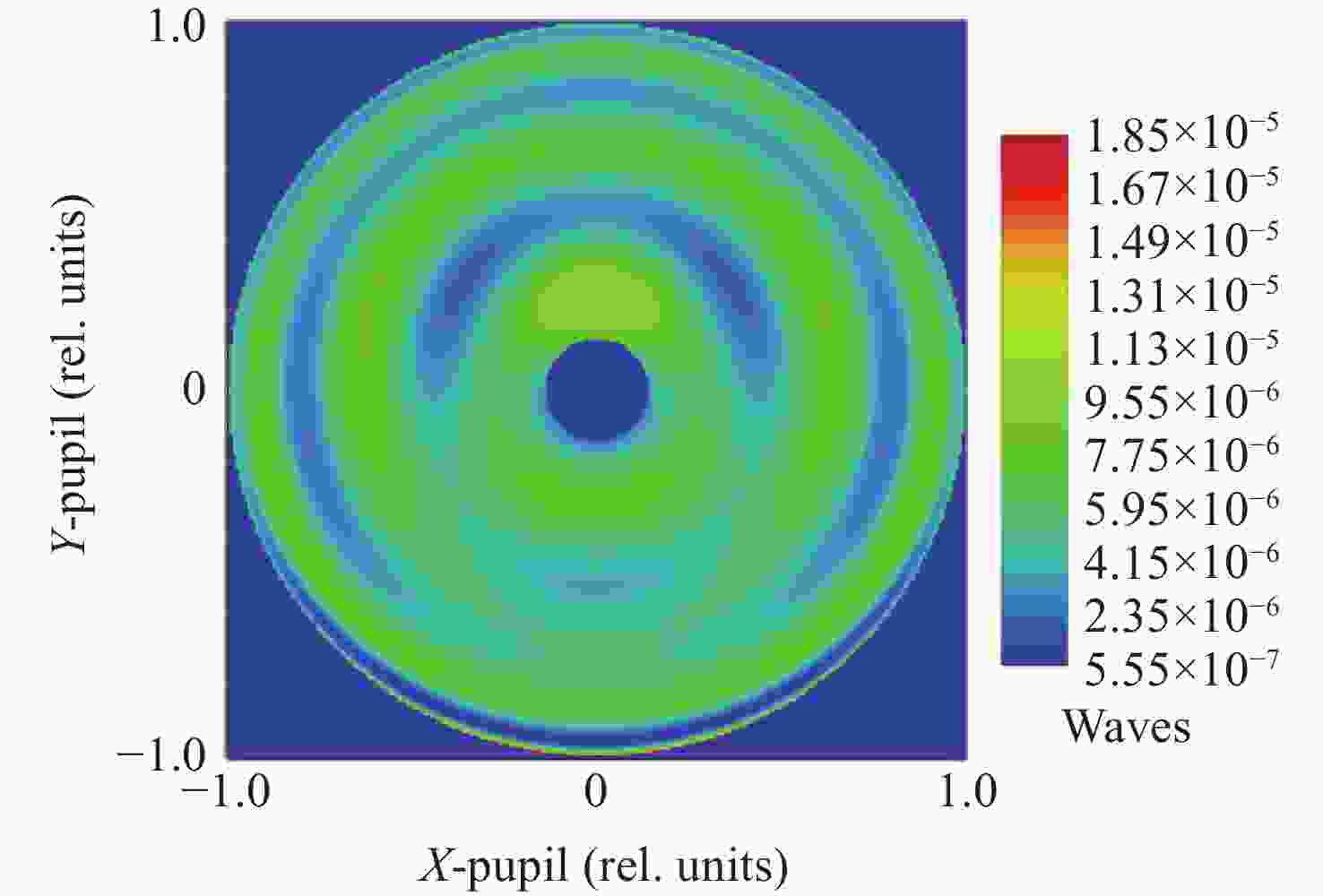
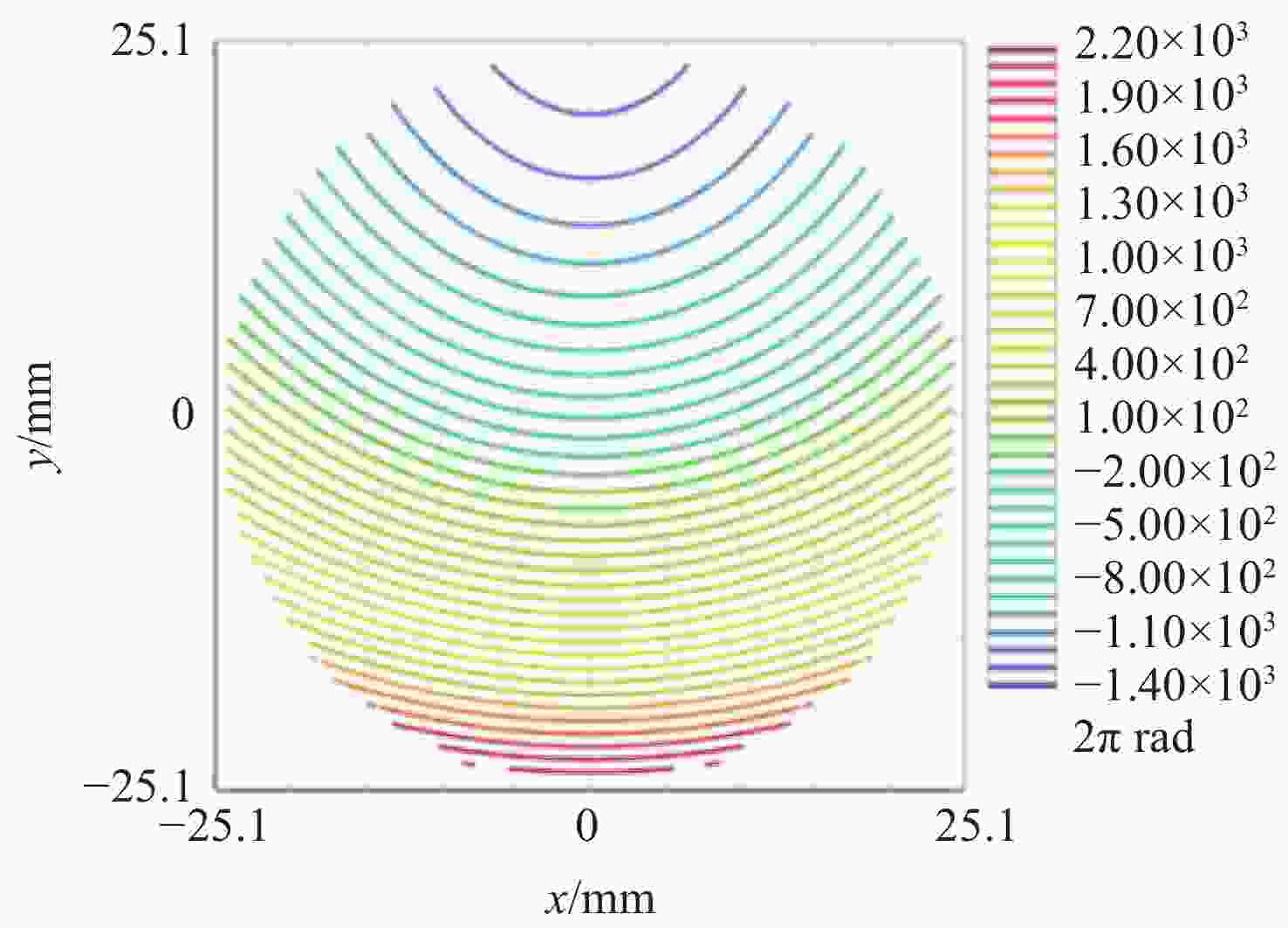
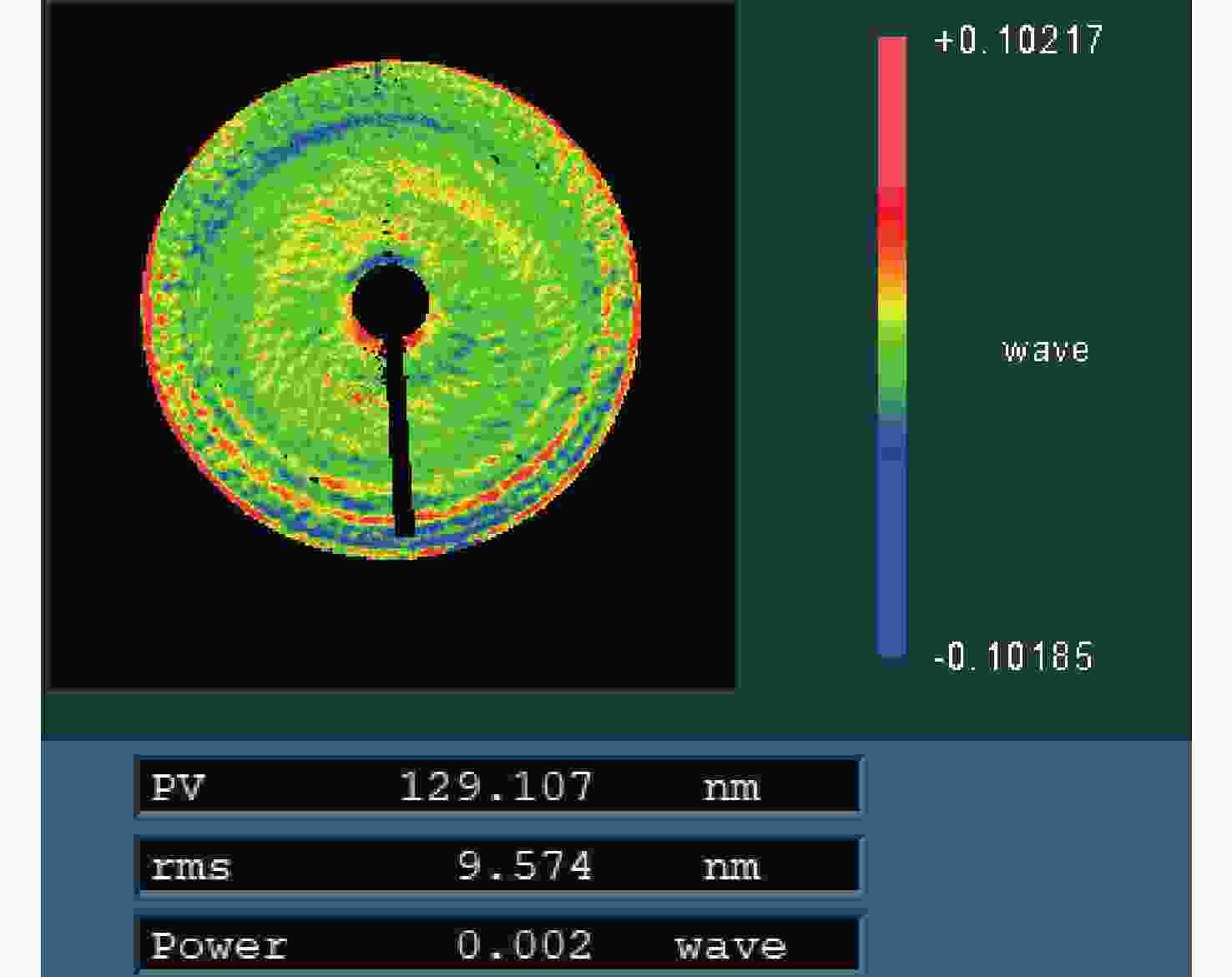
Table 3. Optical design results of main area
参数 数值 区域范围 半径为25.07 mm的圆 检测范围/mm 260 条纹密度估算/(lp·mm−1) 平均值为76,最密处为117.5 干涉仪焦点坐标 F(0, −4),单位mm Zernike拟合残差 rms0.0000λ@632.8 nm 表 4 主镜CGH误差源
Table 4. CGH error sources of the primary mirror
误差项 数值(rms/λ) 备注 设计误差 0.00000 编码误差 0.00010 基板误差 0.0027 假定补偿其Z9及以下低阶项 刻划误差 0.0023 按位置误差σx=σy=30 nm 位置失调误差 0 检测时调整彗差到零 误差合成 0.00355 以RSS方式合成上述各项 -
[1] ZHOU P, BURGE J H. Fabrication error analysis and experimental demonstration for computer-generated holograms[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(5): 657-663. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.000657 [2] LI SH J, ZHANG J, LIU W G, et al. Measurement investigation of an off-axis aspheric surface via a hybrid compensation method[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(28): 8220-8227. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.008220 [3] LIANG Z J, ZHAO H Y, YANG Y Y. Solving optimal carrier frequencies of a CGH null compensator through a double-constrained searching method based on iterative ray-tracings[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(16): 4699-4709. doi: 10.1364/AO.455315 [4] SHEN H, ZHU R H, GAO ZH SH, et al. Design and fabrication of computer-generated holograms for testing optical freeform surfaces[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2013, 11(3): 032201. doi: 10.3788/COL201311.032201 [5] YANG H S, SONG J B, LEE I W, et al. Testing of steep convex aspheric surface with a Hartmann sensor by using a CGH[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(8): 3247-3254. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.003247 [6] LIU H, LU ZH W, LI F Y, et al. Design of a novel hologram for full measurement of large and deep convex aspheric surfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(6): 3120-3126. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.003120 [7] PETERHÄNSEL S, PRUSS C, OSTEN W. Phase errors in high line density CGH used for aspheric testing: beyond scalar approximation[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(10): 11638-11651. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.011638 [8] CUI J P, ZHANG N, LIU J, et al. Testing the mid-spatial frequency error of a large aperture long-focal-length lens with CGH[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(7): 9454-9463. doi: 10.1364/OE.388625 [9] LI M ZH, HU H X, ZHANG X J, et al. Modeling and suppressing the wavefront degeneration in a CGH interferometric null test[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(23): 41508-41523. doi: 10.1364/OE.470808 [10] 徐秋云, 孔令臣. 大口径非球面反射镜零位补偿器误差标定方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2024,61(4):0422001.XU Q Y, KONG L CH. Error calibration method of null correctors for large-aperture aspherical mirrors[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(4): 0422001. (in Chinese). [11] 梁子健, 杨甬英, 赵宏洋, 等. 非球面光学元件面型检测技术研究进展与最新应用[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):161-186. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0143LIANG Z J, YANG Y Y, ZHAO H Y, et al. Advances in research and applications of optical aspheric surface metrology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 161-186. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0143 [12] 胡晨, 魏朝阳, 万嵩林, 等. 基于计算全息图的大口径长焦距离轴抛物面反射镜测量[J]. 中国激光,2024,51(11):1101030.HU CH, WEI CH Y, WAN S L, et al. Measurement of large aperture long focus off-axis paraboloid mirror based on computer generated hologram[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(11): 1101030. (in Chinese). [13] 张誉馨, 黎发志, 闫力松, 等. 结合CGH与辅助透镜的长焦距非球面反射镜检测(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(9):20220384. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220384ZHANG Y X, LI F ZH, YAN L S, et al. Long focal length aspherical mirror testing with CGH and auxiliary lenses (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(9): 20220384. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220384 [14] 王兆明, 栗孟娟, 于秋跃, 等. 两面共体非球面反射镜光轴一致性高精度测量方法研究(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程,2023,52(9):20230476. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230476WANG ZH M, LI M J, YU Q Y, et al. Research on high precision testing method for mirror optical axis of two-sided community aspheric mirror (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(9): 20230476. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230476 [15] 刘佳妮, 陈安和, 李智勇, 等. 小口径深度凸非球面的高精度面形检测[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(9):20220190. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220190LIU J N, CHEN A H, LI ZH Y, et al. High-precision shape measurement technology for convex aspheric with small aperture and large convex asphericity[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(9): 20220190. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220190 [16] 苏航, 王孝坤, 程强, 等. 子孔径拼接和计算全息混合补偿检测大口径凸非球面(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(9):20220576. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220576SU H, WANG X K, CHENG Q, et al. Sub-aperture stiching and CGH mixed compensation for the testing of large convex asphere (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(9): 20220576. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220576 [17] LINDLEIN N. Analysis of the disturbing diffraction orders of computer-generated holograms used for testing optical aspherics[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(16): 2698-2708. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.002698 -





 下载:
下载: