Witnessing quantum phase transition in a non-Hermitian trapped ion system via quantum Fisher information
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0017
-
摘要:
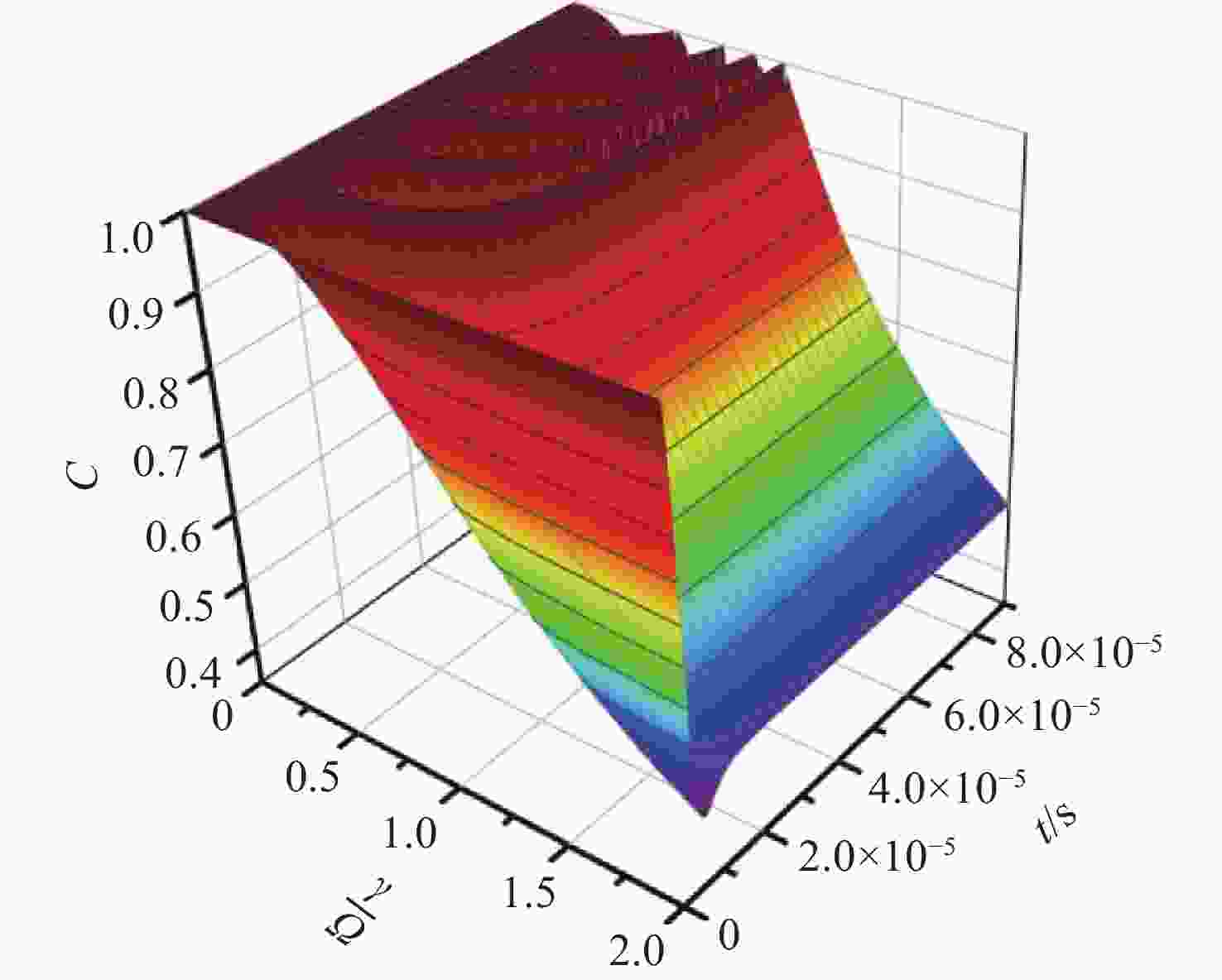
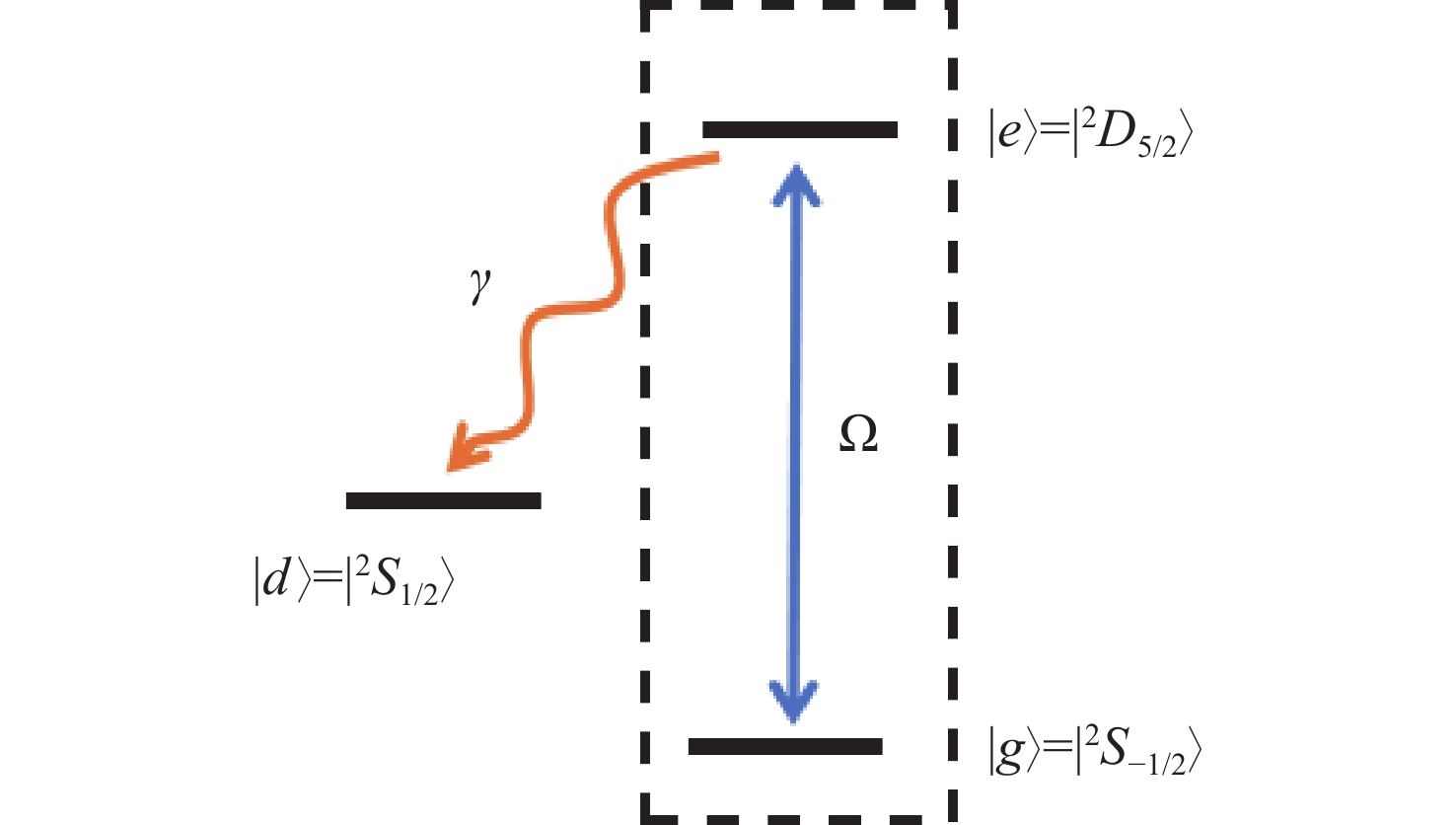
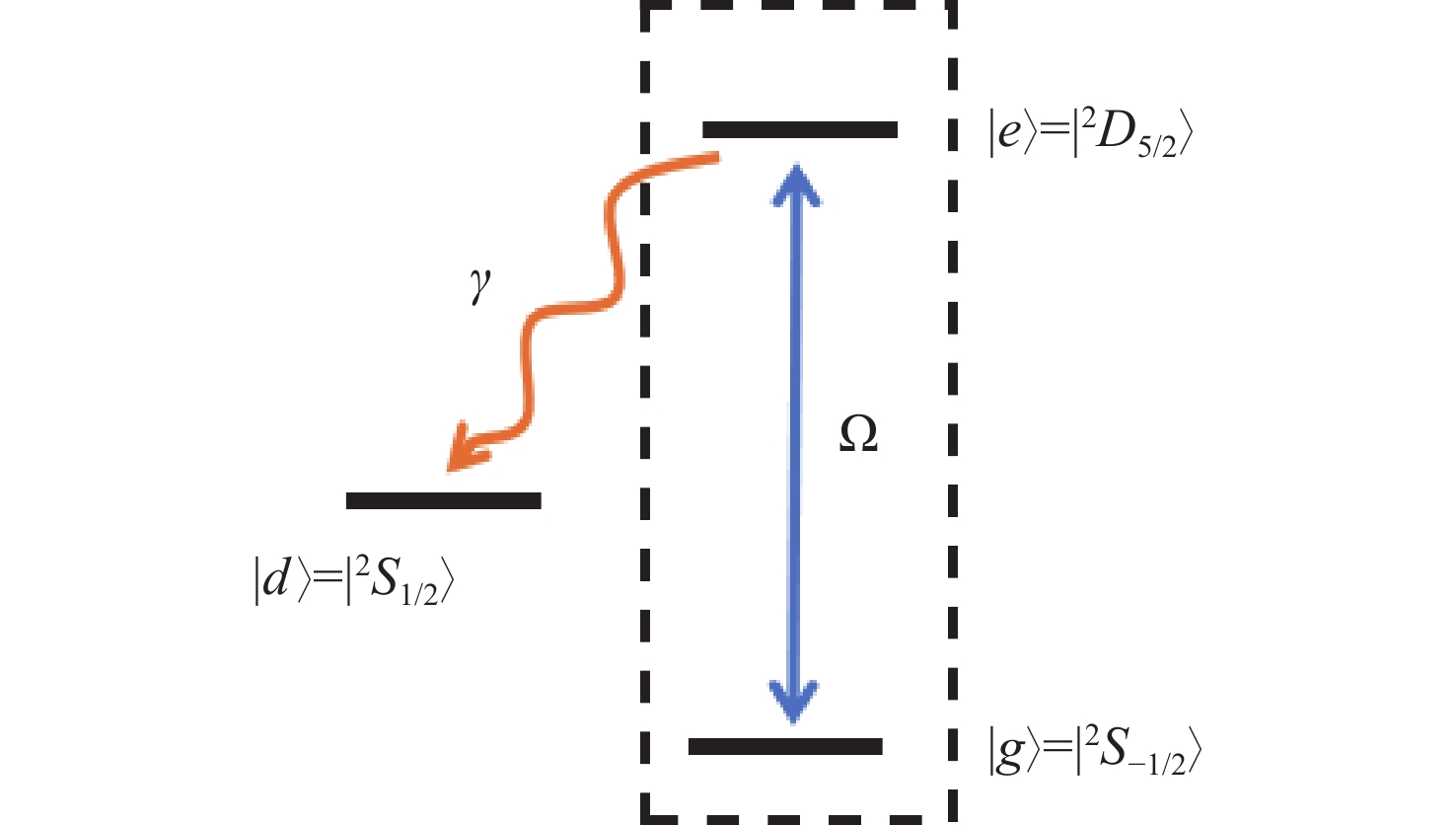
本文以具有增益损耗平衡的非厄米离子阱系统为研究对象,从量子参数测量角度,利用量子Fisher信息量标度非厄米系统的量子相变特征。通过态矢量映射方法,研究了任意两能级非厄米量子系统的一般非幺正演化规律。量子Fisher 信息量的动力学演化在奇异点附近发生突然变化,并定量表征系统的量子临界现象。根据系统物相是否具有宇称和时间反演对称特性,可以获得两种不同行为的演化过程。在对称相区域中,量子Fisher 信息量随时间呈现振荡特征,可获得较高的测量精度。在对称性被破坏的相区域里,它的含时变化经历单调递减过程。这两种动力学行为也被量子熵和量子相干证实。强调了利用量子Fisher信息来见证非厄米离子阱系统的相变。这些结论有助于非厄米量子信息技术发展。
-
关键词:
- PT对称 /
- 非厄米系统 /
- 量子Fisher信息 /
- 量子临界 /
- 离子阱系统
Abstract:Quantum Fisher information is used to witness the quantum phase transition in a non-Hermitian trapped ion system with balanced gain and loss, from the viewpoint of quantum parameter estimation. We formulate a general non-unitary dynamic of any two-level non-Hermitian system in the form of state vector. The sudden change in the dynamics of quantum Fisher information occurs at an exceptional point characterizing quantum criticality. The dynamical behaviors of quantum Fisher information are classified into two different ways which depends on whether the system is located in symmetry unbroken or broken phase regimes. In the phase regime where parity and time reversal symmetry are unbroken, the oscillatory evolution of quantum Fisher information is presented, achieving better quantum measurement precision. In the broken phase regime, quantum Fisher information undergoes the monotonically decreasing behavior. The maximum value of quantum estimation precision is obtained at the exceptional point. It is found that the two distinct kinds of behaviors can be verified by quantum entropy and coherence. Utilizing quantum Fisher information to witness phase transition in the non-Hermitian system is emphasized. The results may have potential applications to non-Hermitian quantum information technology.
-
Key words:
- PT symmetry /
- non-Hermitian system /
- quantum Fisher information /
- quantum criticality /
- ion trap
-
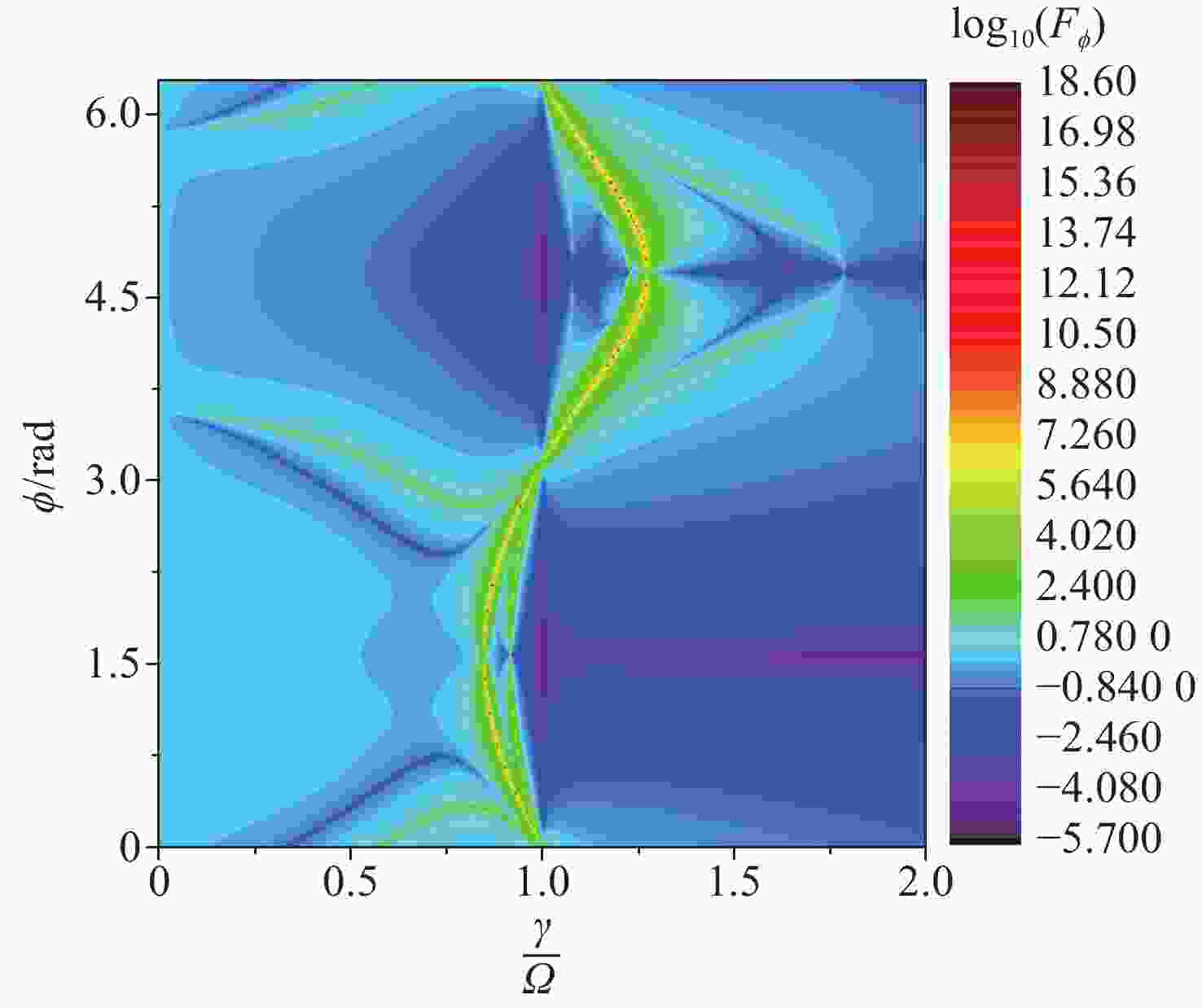
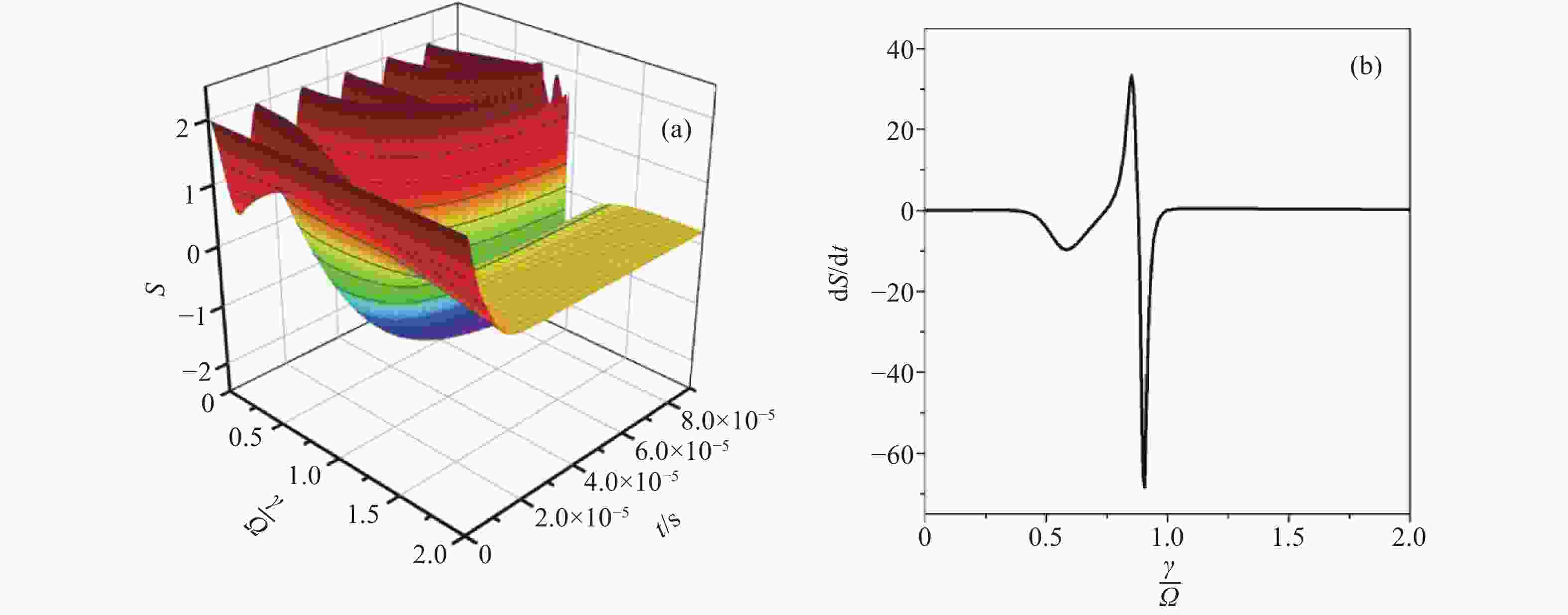
Figure 2. The dynamics of QFI is plotted as a function of the ratio
$\gamma/\varOmega $ in the condition of$\varOmega=2\text{π}\times32\;\mathrm{ kHz}, \theta=\text{π}/2,\phi=0 $ . (a) The contour plot; (b) the oscillation illustrated in the PT symmetry unbroken region of$\dfrac{\gamma}{\varOmega}=0.43 $ ; (c) the decaying behavior in the broken phase of$\dfrac\gamma\varOmega=1.5 $ -
[1] ÖZDEMIR Ş K, ROTTER S, NORI F, et al. Parity–time symmetry and exceptional points in photonics[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(8): 783-798. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0304-9 [2] FENG L, WONG Z J, MA R M, et al. Single-mode laser by parity-time symmetry breaking[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6212): 972-975. doi: 10.1126/science.1258479 [3] SUNADA S. Enhanced response of non-Hermitian photonic systems near exceptional points[J]. Physical Review A, 2018, 97(4): 043804. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.97.043804 [4] LÜ X Y, JING H, MA J Y, et al. PT-symmetry-breaking chaos in optomechanics[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 114(25): 253601. [5] LU T X, ZHANG H L, ZHANG Q, et al. Exceptional-point-engineered cavity magnomechanics[J]. Physical Review A, 2021, 103(6): 063708. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.103.063708 [6] GUO A, SALAMO G J, DUCHESNE D, et al. Observation of PT-symmetry breaking in complex optical potentials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(9): 093902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.093902 [7] CHEN W J, KAYA ÖZDEMIR Ş, ZHAO G M, et al. Exceptional points enhance sensing in an optical microcavity[J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7666): 192-196. doi: 10.1038/nature23281 [8] XU H, LAI D G, QIAN Y B, et al. Optomechanical dynamics in the PT-and broken-PT-symmetric regimes[J]. Physical Review A, 2021, 104(5): 053518. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.104.053518 [9] SU ZH X, YAO E X, HUANG L L, et al. Optical topological characteristics of two dimensional artificial metamaterials[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 955-967. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0074 [10] RANGANI JAHROMI H, LO FRANCO R. Searching for exceptional points and inspecting non-contractivity of trace distance in (anti)-PT symmetric systems[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2022, 21(4): 155. doi: 10.1007/s11128-022-03475-z [11] PIRES D P, MACRÌ T. Probing phase transitions in non-Hermitian systems with multiple quantum coherences[J]. Physical Review B, 2021, 104(15): 155141. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.104.155141 [12] GUO Y N, WANG G Y. Witnessing criticality in non-Hermitian systems via entopic uncertainty relation[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2022, 24: 093035. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/ac91ea [13] BENDER C M, BOETTCHER S, MEISINGER P N. PT-symmetric quantum mechanics[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1999, 40(5): 2201-2229. doi: 10.1063/1.532860 [14] LU X M, WANG X G, SUN C P. Quantum Fisher information flow and non-Markovian processes of open systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2010, 82(4): 042103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.82.042103 [15] ZHONG W, SUN ZH, MA J, et al. Fisher information under decoherence in Bloch representation[J]. Physical Review A, 2013, 87(2): 022337. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.87.022337 [16] YU X L, ZHANG CH J. Quantum parameter estimation of non-Hermitian systems with optimal measurements[J]. Physical Review A, 2023, 108(2): 022215. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.108.022215 [17] ZLOSHCHASTIEV K G. Non-Hermitian Hamiltonians and stability of pure states[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2015, 69(11): 253. doi: 10.1140/epjd/e2015-60384-0 [18] MINGANTI F, MIRANOWICZ A, CHHAJLANY R W, et al. Quantum exceptional points of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians and Liouvillians: the effects of quantum jumps[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 100(6): 062131. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.100.062131 [19] WANG W CH, ZHOU Y L, ZHANG H L, et al. Observation of PT-symmetric quantum coherence in a single-ion system[J]. Physical Review A, 2021, 103(2): L020201. [20] MIRI M A, ALÙ A. Exceptional points in optics and photonics[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6422): eaar7709. [21] SERGI A, GIAQUINTA P V. Linear quantum entropy and non-Hermitian Hamiltonians[J]. Entropy, 2016, 18(12): 451. doi: 10.3390/e18120451 [22] SERGI A, ZLOSHCHASTIEV K G. Quantum entropy of systems described by non-Hermitian Hamiltonians[J]. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 2016, 2016: 033102. doi: 10.1088/1742-5468/2016/03/033102 [23] BAUMGRATZ T, CRAMER M, PLENIO M B. Quantifying coherence[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(14): 140401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.140401 [24] STRELTSOV A, ADESSO G, PLENIO M B. Colloquium: quantum coherence as a resource[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2017, 89(4): 041003. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.89.041003 -





 下载:
下载: