-
摘要: 空间激光通信凭借其带宽优势,成为未来高速空间通信不可或缺的有效手段,是近年来国际上的研究热点。本文详细介绍了美国、欧洲和日本在空间激光通信技术领域的最新研究进展和未来发展规划,总结了国内外空间激光通信演示计划的主要参数指标。通过对空间激光通信最新研究计划的分析,归纳出空间激光通信高速化、深空化、集成化、网络化、一体化5个发展趋势,以及需要突破的高阶调制、高灵敏度探测、多制式兼容、"一对多"通信等关键技术。为我国激光通信设备及相关研究提供借鉴和参考。Abstract: Free-space laser communication, by virtue of its bandwidth advantage, has become an indispensable and effective means for high-speed space communication in the future, and is a research hotspot in recent years. This paper gives a detailed introduction in the latest research progress and future development planning of free-space laser communication technology in the United States, Europe and Japan, and summarizes the main parameters of the free-space laser communication demonstration program at home and abroad. Through deep analysis of the latest research plan of free-space laser communication, we summarize five future development trends of free-space laser communication, namely high-speed, deep-space, multifunction, networking, and integration, as well as key technologies that are expected to break through, such as high-order modulation, high-sensitivity detection, multi-system compatibility and "one-to-many" communication. These technologies provide guidance and reference for free-laser communication equipment and related research in China.
-
表 1 空间激光通信演示计划
Table 1. Space laser communication demonstrations timeline
美国 欧洲 日本 中国 过去空间激光通信试验 ●1995:GOLD(NASA JPL), GEO-GND, 0.8/0.5 μm, IMDD, 1 Mbps;
● 2001: GeoLITE(NRO), GEO-GND
● 2013:LRO(NASA GSFC), Lunar-GND, 1 064.3 nm, PPM, 300 bps;
● 2013:LLCD(NASA GSFC), Lunar-GND, 1 550 nm, PPM, 622 Mbps;
● 2014:OPALS(NASA JPL), ISS-GND, 1 550 nm, IMDD, 30~50 Mbps;●2001:SILEX(ESA), GEO-LEO, GEO-GND, 0.8 μm, IMDD, 50 Mbps;
●2006:LOLA(ESA), GEO-Air, 0.8 μm, IMDD, 50 Mbps;
●2008:NFIRE(DLR), LEO-LEO, LEO-GND, 1 064 nm, BPSK, 5.6 Gbps;
●2016:EDRS-A(ESA), GEO-LEO, GEO-GND, 1 064 nm, BPSK, 1.8 Gbps●1994: ETS-VI(NICT), GEO-GND, 0.8/0.5 μm, IMDD, 1 Mbps
●2006: OICETS(JAXA/NICT), LEO-GEO, LEO-GND, 0.8 μm, IMDD, 50 Mbps;
●2014: SOTA(NICT), LEO-GND, 980/1 550 nm, IMDD, 10 Mbps●2011:海洋2号(哈工大), LEO-GND, 1 550 nm, IMDD, 504 Mbps;
●2016:墨子号(上海光机所),LEO-GND,1 550 nm, DPSK/PPM, 5.12 G/20 Mbps;
●2016:天宫二号(武汉大学),LEO-GND,1 550 nm, IMDD, 1.6 Gbps;
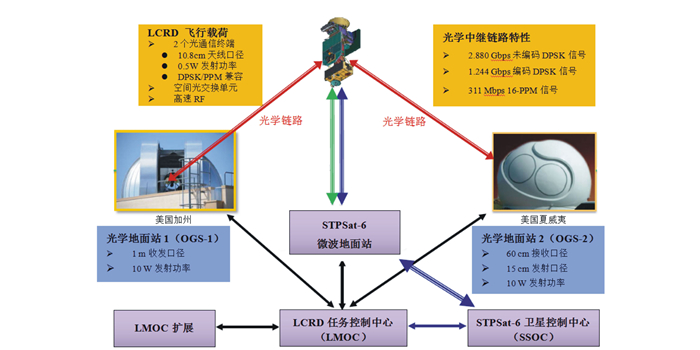
●2017:实践十三号(哈工大), GEO-GND,1 550 nm, IMDD, 2.5 Gbps未来计划 ●2019:LCRD(NASA GSFC), GEO-GND, 1 550 nm, DPSK/PPM, 2.8 G/622 Mbps;
●2021:ILLUMA-T(NASA GSFC), LEO-GEO-GND, 1 550 nm, DPSK/PPM, 2.8 G/622 Mbps;
●2023:DSOC(NASA JPL), Mars-GND, 1 060/1 550 nm, PPM, 2k/264 Mbps●2018:EDRS-C(ESA), GEO-LEO, GEO-GND, 1 064 nm, BPSK, 1.8 Gbps;
●2018:OPTEL-μ(RUAG), LEO-GND, 1 550 nm, IMDD, 2 Gbps;
●2020:OPTEL-D(ESA), Deep space-GND, 1 064/1 550 nm, PPM, 192 kMbps●2018: VSOTA(NICT), LEO-GND, 980/1 550 nm, IMDD, 1k/100 kbps;
●2019:JDRS(JAXA/ NICT), GEO-GND, 1 550 nm, DPSK/ IMDD, 1.8 G/50 Mbps;
●2021:HICALI(NICT), GEO-GND,1 550 nm, 10 Gbps表 2 AIM光通信系统的主要参数
Table 2. Key design parameters of AIM optical communication system
参数 地面站 AIM 海拔 2 393 m 7 500~1 500万千米 接收孔径 1 016 mm 135 mm 接收波长 1 550 nm 1 064 nm 接收滤波器带宽 5 nm 5 nm 接收端有效焦距 13 300 mm 135 mm 发射波长 1 064 nm 1 550 nm 发射孔径 250 mm 135 mm 发射信号制式 NA 16 PPM 发射速率 None 195 kpbs 发射功率 2.4 kW 3 W 表 3 JDRS和光学数据中继系统技术规格
Table 3. Specifications of JDRS and optical data relay system
分系统 参数 规格 JDRS 运载火箭 H-IIA 发射年份 2019年 卫星轨道位置 90.75°E 任务期限 10年 数据中继系统 速率 返向1.8 Gbps,前向50 Mbps 误码率* 返向1E-5,前向1E-6 LEO卫星 高度200~1 000 km 光学链路 波长 返向1 540 nm,前向1 560 nm 调制/解调 返向RZ-DPSK-DD,前向IM/DD 捕获时间 <60 s 光学天线口径 GEO:15 cm,LEO:10 cm 馈线链路 频率 Ka波段 调制/解调 返向16QAM,前向QPSK 复用方式 频率或偏振(返回连路) *光链路和馈线链路的总误码率. -
[1] STEVEN C, LAURA E E, MARK L S, et al.. Design of a High-Speed Space Modem for the Lunar Laser Communications Demonstration[J]. Proc. of SPIE, 2011, 7923:792308. doi: 10.1117/12.878927 [2] SUN X L, DAVID R S, EVAN D H, et al.. Free space laser communication experiments from earth to the lunar reconnaissance orbiter in lunar orbit[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(2):1865-1871. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.001865 [3] ROBERTS W T. Discovery deep space optical communications(DSOC) transceiver[J]. Proc. of SPIE, 2017, 10096:VNSP100960V. doi: 10.1117/12.2256001 [4] 姜会林, 安岩, 张雅琳, 等.空间激光通信现状、发展趋势及关键技术分析[J].飞行器测控学报, 2015, 34(3):207-217. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxqckxb201503001JIANG H L, AN Y, ZHANG Y L, et al.. Analysis of the status quo, development trend and key technologies of space laser communication[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2015, 34(3):207-217.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxqckxb201503001 [5] 吴从均, 颜昌翔, 高志良.空间激光通信发展概述[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(5):670-680. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9051.shtmlWU C J, YAN CH X, GAO ZH L. Overview of space laser communications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(5):670-680. (in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9051.shtml [6] 曾飞, 高世杰, 伞晓刚, 等.机载激光通信系统发展现状与趋势[J].中国光学, 2016, 9(1):65-73. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9388.shtmlZENG F, GAO SH J, SAN X G, et al.. Development status and trend of airborne laser communication terminals[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(1):65-73.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9388.shtml [7] 李少辉, 陈小梅, 倪国强.高精度卫星激光通信地面验证系统[J].光学精密工程, 2017, 25(5):1149-1158. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201705005LI SH H, CHEN X M, NI G Q. Highly precise ground certification system of satellite laser communication[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2017, 25(5):1149-1158.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201705005 [8] MORIO T, TETSUHARU F, DIMITAR R K, et al.. Current status of research and development on space laser communications technologies and future plans in NICT[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications(ICSOS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2015: 1-5. [9] 于笑楠, 佟首峰, 董岩, 等.空间激光通信组网单光束跟踪子系统[J].光学精密工程, 2014, 22(12):3348-3353. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201412027YU X N, TONG SH F, DONG Y, et al. Single beam tracking subsystem of space laser communication network[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2014, 22(12):3348-3353.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201412027 [10] KNUT B, MARK G, FRANK H, et al.. Laser communication terminals for the European Data Relay System[J]. Proc. of SPIE, 2012, 8246:82460D. doi: 10.1117/12.906798 [11] HERWIG Z, FRANK H, MATTHIAS M. Laser communication terminal: product status and industrialization process[C]. Proc. International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications(ICSOS), Kobe, Japan, 2014, S6-3. [12] 付强, 姜会林, 王晓曼, 等.空间激光通信研究现状及发展趋势[J].中国光学, 2012, 5(2):116-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.02.004FU Q, JIANG H L, WANG X M, et al.. Research status and development trend of space laser communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(2):116-125.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.02.004 [13] 张靓, 郭丽红, 刘向南, 等.空间激光通信技术最新进展与趋势[J].飞行器测控学报, 2013, 32(4):286-293. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxqckxb201304002ZHANG L, GUO L H, LIU X N, et al.. Latest progress and trends of development of space laser communication[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2013, 32(4):286-293.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxqckxb201304002 [14] LUZHANSKIY E, EDWARFS B, ISRAEL D, et al.. Overview and status of the laser communication relay demonstration[J]. Free-Space Laser Communication and Atmospheric Propagation XXVⅢ, 2016, 9739:97390C. doi: 10.1117/12.2218182 [15] JADE P W, BROWNE C A, BURTON C D, et al.. Performance and qualification of a multi-rate DPSK modem[J]. Proc. of SPIE, 2014, 8971:89710Z. doi: 10.1117/12.2057577 [16] CORNWELL D. Space-based laser communications break threshold[J]. Optics and Photonics News, 2016, 27(5):24-31. doi: 10.1364/OPN.27.5.000024 [17] BISWAS A, KOVALIK J M, SRINIVASAN M, et al.. Deep space laser communications[J]. Proc. SPIE, 2016, 9739:97390Q. doi: 10.1117/12.2217428 [18] ROBERTS W T. Discovery deep space optical communications(DSOC) transceiver[J]. Proc. of SPIE, 2017, 10096:100960V-1. doi: 10.1117/12.2276289 [19] MIGLIORE R, DUNCAN J, PULCINO V, et al.. Outlook on EDRS-C[C]. International Conference on Space Optics 2016, 2017, 10562: 105622S. [20] 车晓杰, 梁忠诚, 刘学明.室内MIMO可见光通信的接收特性[J].发光学报, 2016, 37(2):242-249. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201602019CHE X J, LIANG ZH CH, LIU X M. Receiving characteristics of indoor MIMO visible light communication[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 37(2):242-249.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201602019 [21] BAISTER G, GREGER R, BACHER M, et al.. OPTEL-μ LEO to ground laser communications terminal:flight design and status of the EQM development project[J]. International Conference on Space Optics 2016. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2017, 10562:105622U. doi: 10.1117/12.2296075 [22] DREISCHER T, THIEME B, BACHER M, et al.. OPTEL-μ:a compact system for optical downlinks from LEO satellites[J]. Proc. 12th Space Ops, Stockholm, Sweeden, 2012. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0212468999/ [23] HEESE C, SODNIK Z, CARNELLI I. Design of the optical Communication system for the asteroid impact mission[C]. International Conference on Space Optics 2016, 2017, 10562: 105622W. [24] YAMAKAWA S, CHISHIKI Y, SASAKI Y, et al.. JAXA's optical data relay satellite programme[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications(ICSOS), IEEE, 2015: 1-3. [25] CHISHIKI Y, YAMAKAWA S, TAKANO Y, et al.. Overview of optical data relay system in JAXA[J]. Proc. of SPIE, 2016, 9739:97390D-1. doi: 10.1117/12.2239310 [26] FUSE T, AKIOKA M, KOLEV D, et al.. Development of a breadboard model of space laser communication terminal for optical feeder links from Geo[C]. International Conference on Space Optics 2016. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2017, 10562: 105622X. [27] TOYOSHIMA M, FUSE T, KOLEV D R, et al.. Current status of research and development on space laser communications technologies and future plans in NICT[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications(ICSOS) IEEE, 2015: 1-5. -






 下载:
下载: