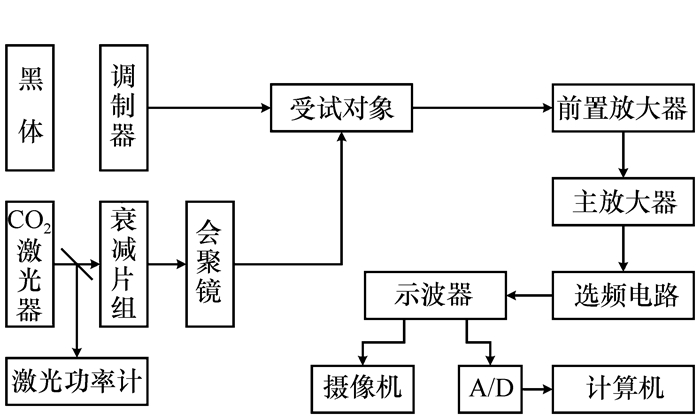
-
摘要: 本文针对高重频CO2激光干扰技术展开分析和研究。首先,概述了激光对抗武器的概念、分类和特点,以及激光对抗武器的干扰与破坏的主要目标对象。其次,分析了红外探测器激光干扰损伤效果的检测方法。再次,分析了光学元件激光变形损伤效果的检测方法以及光学薄膜的激光损伤检测方法。按照上述检测方法进行实验,分别对红外单元探测器、光学元件、光学薄膜和其他材料的激光损伤阈值实验数据进行分析与讨论。最后,总结了全文并且展望了激光干扰技术的发展。Abstract: This paper analyzes and studies the interference technology of the high repetition frequency CO2 laser. First of all, the conception, classification and characteristic of the laser weapon as well as the main interference and destruction objects are summarized. Secondly, the detection method of laser interference and destruction effect of the infrared detectors is analyzed. Thirdly, this paper focuses on the analysis of the detection method of laser deformation damage of the optical components. Then, the laser damage detection method of the optical thin film is mainly described. In addition, experiments are carried out in accordance with the above detection methods, and the laser damage threshold experimental data of infrared unit detectors, optical components, optical thin film and other materials are analyzed and discussed. Finally, the laser interference technology is prospected.
-
表 1 不同对象的激光损伤阈值数据
Table 1. Data of laser damage thresholds for different objects
类型 受试对象
名称激光与光路参数 受试对象
参数损伤阈值(W/ cm2) 说明 λ、F、τ 照射时
间/s会聚光斑
直径/mm干扰 破坏 其它 红
外
探
测
器HgCdTe(PC)
10.6 μm0.75~4 1~1.4 D*:5.3×109~
8.9×101017~22 174~221 HgCdTe(PV) 300 Hz
0.2 ms1 1.4 D*:(2.8~
4.8)×1090.64~0.65 6.5 InSb 2.4~2.9 1.2~1.4 D*:(2.7~
6.5)×10920~25 200~245 热释电器件 0.75~4.8 D*:(1.8~
2)×1081.3 13 红
外
热
像
仪HR-2
红外热像仪
10.6μm4~5 0.2 D*:2.2×1010 0.04 严重
干扰
≥300
~900干扰阈值:
出现麻点;
严重干扰:
出现饱和
和亮线光
学
材
料光学透镜 300 Hz
0.2 ms4~5 11~28 直径:
15~50 mm
厚度:
2.39 mm;
直径: 48 mm
厚度:2.3 mm12~32 变形
91~113照射2~5
次碎裂,
形变量
0.3~
0.4 mm氟化钡 4.5~4.8 2 厚度3 mm 31 出裂纹 氟化镁 3~4.7 2 Φ 20×1.6 mm 11~14.8 打成三块 薄
膜光学薄膜
ZnS-A9-ZnSe10.6 μm
300 Hz
0.2 ms5 1.6 200 硬
材
料玻璃钢
铝镁合金10.6 μm
300 Hz
0.2 ms4~5
4~52.2~3.5
1~2烧蚀
8~12烧出炕
无法破坏表 2 几种激光器损伤阈值比较
Table 2. Comparison of damage thresholds for different type of lasers
参数 重频(300 Hz)CO2激光 单脉冲CO2激光 连续CO2激光 HgCdTe(PC)/(W·cm-2) (1~2)×102 8×107 ≥103 照射时间/μs 75~4 1 ≥106 脉冲宽度/μs 0.2 1 表 3 CO2激光破坏导弹导引头材料实验数据
Table 3. Experimental data of missile seeker materials destroyed by CO2 laser
材料 厚度/mm 作用激光功率/W 作用面积/cm2 功率密度/(W·cm-2) 作用时间/s 作用效果 备注 K8 2 490 4.90 100 2.8 炸裂 远场破坏 K8 3 562 4.90 114.7 3 炸裂 远场破坏 K9 5 570 4.90 116.3 5 炸裂 远场破坏 MgF2 3 505 4.90 103.3 2 炸裂 远场破坏 MgF2 3 730 2.38 211 0.428 炸裂 远场破坏 MgF2 6 1 474 3.0 438 0.224 炸裂 近场破坏 K9 4 905 2.63 344.1 0.896 炸裂 近场破坏 K9 6 1 463 3.05 556 0.768 炸裂 近场破坏 玻璃钢 3 2 100 3.57 588.2 3 炸裂 头罩实物 玻璃钢 3 3 000 2 炸裂 头罩实物 -
[1] 刘志春, 孙玉铭, 苏震, 等.国外激光干扰技术的发展[J].舰船电子工程, 2009, 29(7):21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2009.07.006LIU ZH CH, SUN Y M, SU ZH, et al.. Development of the foreign laser interference technology[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2009, 29(7):21-24.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2009.07.006 [2] 朱孟真, 程勇, 谭朝勇, 等.国外空间激光的发展现状[J].红外与激光工程, 2012, 41(12):3241-3248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.12.020ZHU M ZH, CHENG Y, TAN CH Y, et al.. Development of foreign spaceborne laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2012, 41(12):3241-3248.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.12.020 [3] 汤伟, 郭劲, 邵俊峰, 等.激光重频对脉冲非稳腔TEA CO2激光远场传输特性的影响分析[J].红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(9):2380-2385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.09.015TANG W, GUO J, SHAO J F, et al.. Analysis of far-field characteristics with repetition frequency of TEA CO2laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(9):2380-2385.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.09.015 [4] 解晓辉, 廖清君, 杨勇斌, 等.HgCdTe甚长波红外光伏器件的光电性能[J].红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(5):1141-1145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.05.006XIE X H, LIAO Q J, YANG Y B, et al.. Electro-optical characteristics of HgCdTe very long wavelength infrared photovoltaic detector[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(5):1141-1145.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.05.006 [5] 王思雯, 郭立红, 赵帅, 等.高功率CO2激光对远场HgCdTe探测器的干扰实验[J].光学精密工程, 2010, 18(4):798-804. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201004005WANG S W, GUO L H, ZHAO SH, et al.. Experiments of high-power CO2 laser disturbance to far-field HgCdTe detectors[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2010, 18(4):798-804.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201004005 [6] 王挺峰, 汤伟, 邵俊峰, 等.高重复频率CO2激光重复频率大小对HgCdTe晶体温升及损伤特性影响分析[J].中国激光, 2015, 42(2):0206006. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201502031.htmWANG T F, TANG W, SHAO J F, et al.. Analysis of temperature and damage characteristics of HgCdTe crystal on repetition frequency of CO2 laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(2):0206006.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201502031.htm [7] 汤伟, 邵俊峰, 赵帅, 等.高重频CO2激光对Hg0.826Cd0.174Te晶体的损伤[J].红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(10):2663-2668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.10.013TANG W, SHAO J F, ZHAO SH, et al.. Hg0.826Cd0.174Te crystal damaged by high repetition frequency CO2 laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(10):2663-2668.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.10.013 [8] 汤伟, 吉桐伯, 郭劲, 等.高重频CO2激光损伤HgCdTe晶体的数值分析[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(5):736-742. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9058.shtmlTANG W, JI T B, GUO J, et al.. Numerical analysis of HgCdTe crystal damaged by high repetition frequency CO2 laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(5):736-742.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9058.shtml [9] 徐向晏, 陆卫, 陈效双, 等.光伏型长波HgCdTe红外探测器的数值模拟研究[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2006, 25(4):251-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2006.04.003XU X Y, LU W, CHEN X SH, et al.. Numerical simulation of long wavelength photovoltaic HgCdTe photodiodes[J]. Infrared Millim Waves, 2006, 25(4):251-256.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2006.04.003 [10] 王玺, 卞进田, 李华, 等.重频脉冲CO2激光损伤K9玻璃的实验[J].红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(5):1204-1207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.05.018(in Chinese) WANG X, BIAN J T, LI H, et al.. Experiment on damage in K9 glass due to repetition rate pulsed CO2 laser radiation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(5):1204-1207.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.05.018 -






 下载:
下载: