Current Issue
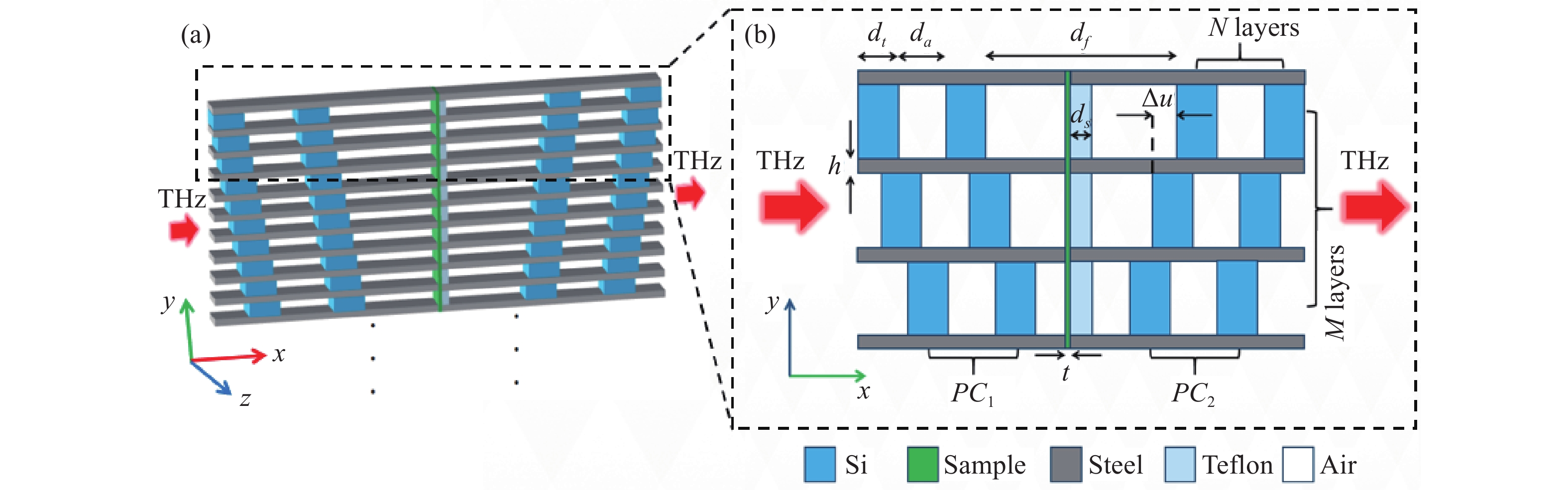
Terahertz (THz) spectroscopy technology has demonstrated great application value in the field of organic and biological macromolecule detection. However, the traditional sample pressing method cannot be applied in the actual detection of trace analytes, and additional structures are required to enhance the interaction between the analytes and THz waves. To solve this problem, we propose a terahertz absorption spectrum enhancement structure based on stacked one-dimensional photonic crystals (1D-PCs) defect cavities. The structure employs metal parallel-plate waveguides to separate a series of one-dimensional photonic crystals (1D-PCs) with defect cavities of varying widths, and coats the sample film on a substrate that penetrates all defect cavities. The incident broadband terahertz wave can simultaneously excite multiple resonant peaks at different frequencies corresponding to the photonic crystal defect modes in different layers. The enhanced terahertz absorption spectrum of the analyte can be obtained by linking the envelope formed by these resonant absorption peaks. The simulation results show that a 0.1 μm α-lactose sample can accomplish an absorption enhancement factor of approximately 303 times in the frequency range of 0.49 to 0.57 THz. This method offers fast measurement speed and maintains a relatively low sample amount, providing an effective strategy for the enhancement detection of trace analytes by terahertz absorption spectrum.
Limited by the diffraction limit, the spatial resolution of traditional microwave antennas is difficult to break through the constraint of the wavelength scale, which hinders their application in high-resolution microwave sensing and detection. In this paper, we design an all-dielectric integrated meta-antenna beyond the physical diffraction limit. Firstly, the meta-antenna is functionalized using asymmetric scattering metagrating array based on the generalized Snell's law. High-efficiency focusing beam in the sub-wavelength scale is obtained by manipulating the electromagnetic wavefront. Then, by optimizing the geometric structure of the metagrating to achieve high manipulation efficiency. Finally, the electric field intensity distribution of the generated focal spot is analyzed. The simulation results demonstrate that the manipulation and diffraction efficiencies of the metalens reach 98.50% and 72.56%. The metalens shows a focal spot with the diameter of 0.73λ and depth of focus (DOF) of 15.11λ. The designed meta-antennas possess the characteristics of long focal depth and high efficiency. Its sub-wavelength focusing property significantly enhances the spatial resolution, which provides a new method for high-precision sensing and detection in the fields such as microwave imaging and non-destructive testing, possessing potential application value.
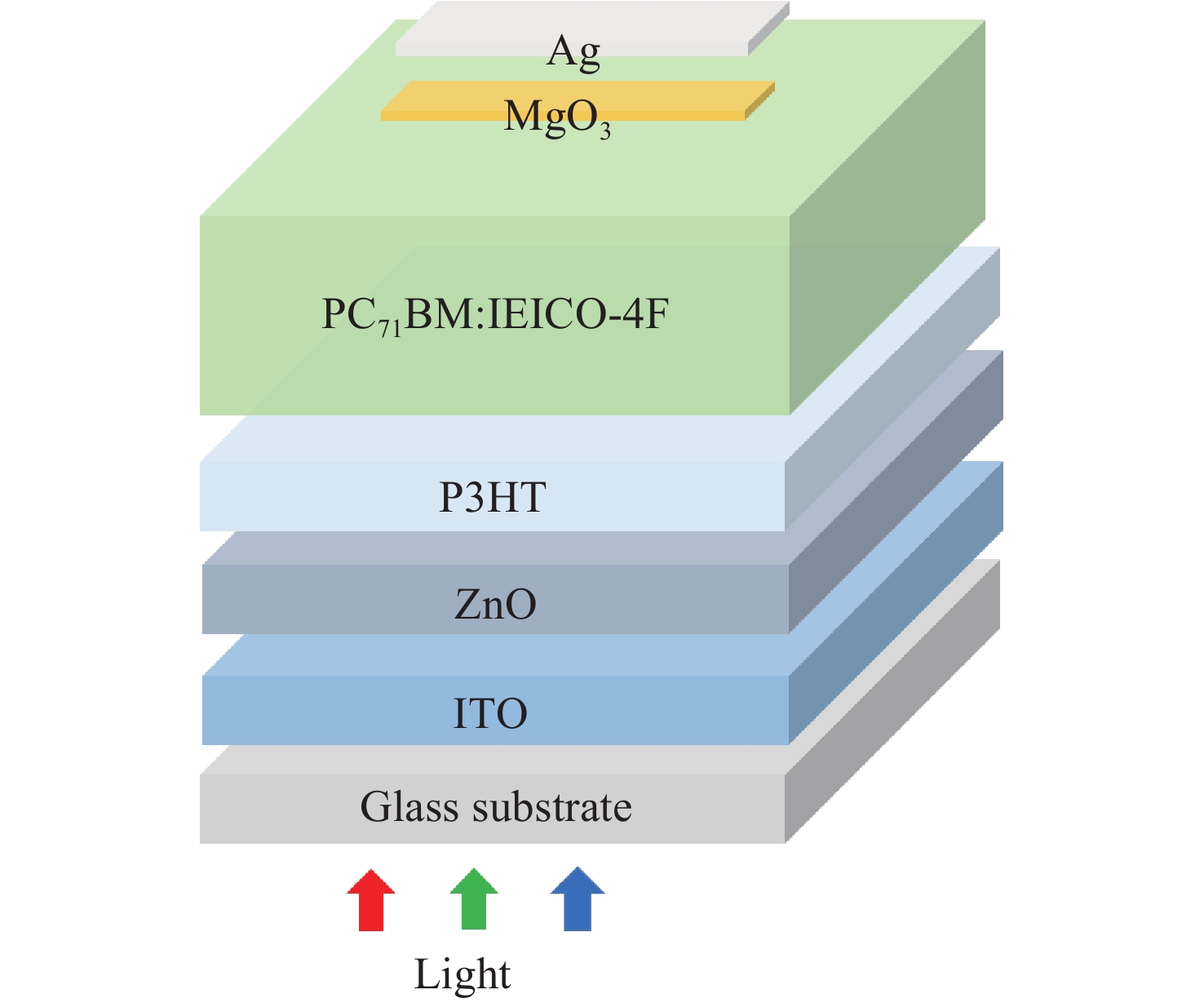
This study investigates the impact of doping the non-fullerene small molecule IEICO-4F into the acceptor component of a planar heterojunction organic photodetector based on the P3HT : PC71BM system on the device's optoelectronic properties. The active layer films with different doping ratios were fabricated using a solution process. Characterization techniques including current-voltage measurements, external quantum efficiency, ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared absorption spectroscopy, and photoluminescence spectroscopy were employed, combined with atomic force microscopy to analyze morphological evolution. Experimental results demonstrate that the introduction of IEICO-4F significantly broadens the absorption spectrum of the active layer into the near-infrared region (700−900 nm) and enhances photon capture efficiency through complementary absorption spectrum. At an optimized doping ratio of 30%, the device's photocurrent density increases from 19.17 mA/cm2 to 27.25 mA/cm2, and the specific detectivity improves from 0.78×1012 Jones to 1.45×1012 Jones. Morphological analysis confirms that IEICO-4F optimizes the phase distribution of PC71BM, forming a finer interpenetrating network structure that facilitates charge transfer and reduces series resistance. The study also reveals that excessive doping disrupts the phase separation balance, adversely affecting carrier separation and transport, leading to an imbalance in electron-hole transport. This work highlights the multifaceted regulatory effect of non-fullerene acceptor doping on traditional polymer: fullerene systems, effectively enhancing device performance through the synergistic mechanisms of spectral broadening and morphological optimization, thereby providing new insights for the design of organic photodetector material systems.
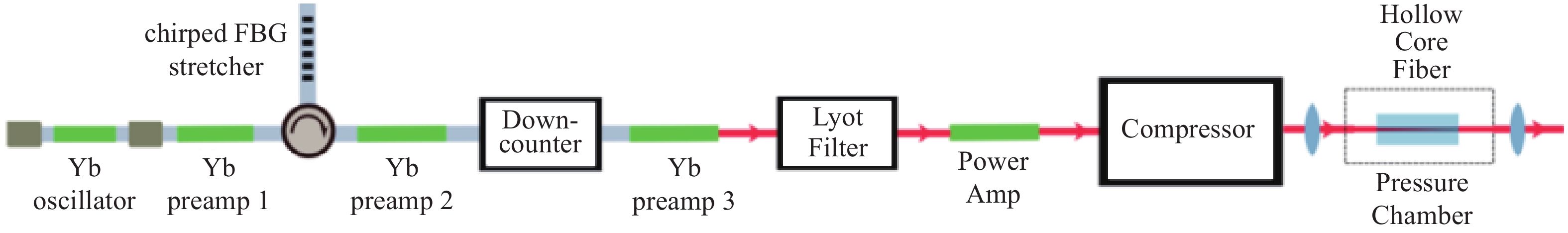
In recent years, ultrafast fiber laser coherent beam combination (CBC) has developed rapidly, becoming an important technical means for enhancing the average power of ultrafast and ultra-intense lasers. However, due to factors such as spectral gain narrowing in single-channel fiber amplifiers and high-order dispersion mismatch, the output pulse width of high-power ultrafast fiber laser CBC systems is significantly wider compared to that of bulk solid-state laser systems, severely limiting its peak power enhancement. From the perspective of pulse compression in ultrafast fiber laser coherent combining, this review systematically analyzes the following three aspects: pulse shaping technique based on fiber chirped pulse amplification, combining technique based on fiber nonlinear spectral broadening, and coherent spectral combining technique based on partial spectral interference. Additionally, a brief conclusion and outlook on the future development of ultra-short pulse fiber laser CBC is given at the end.
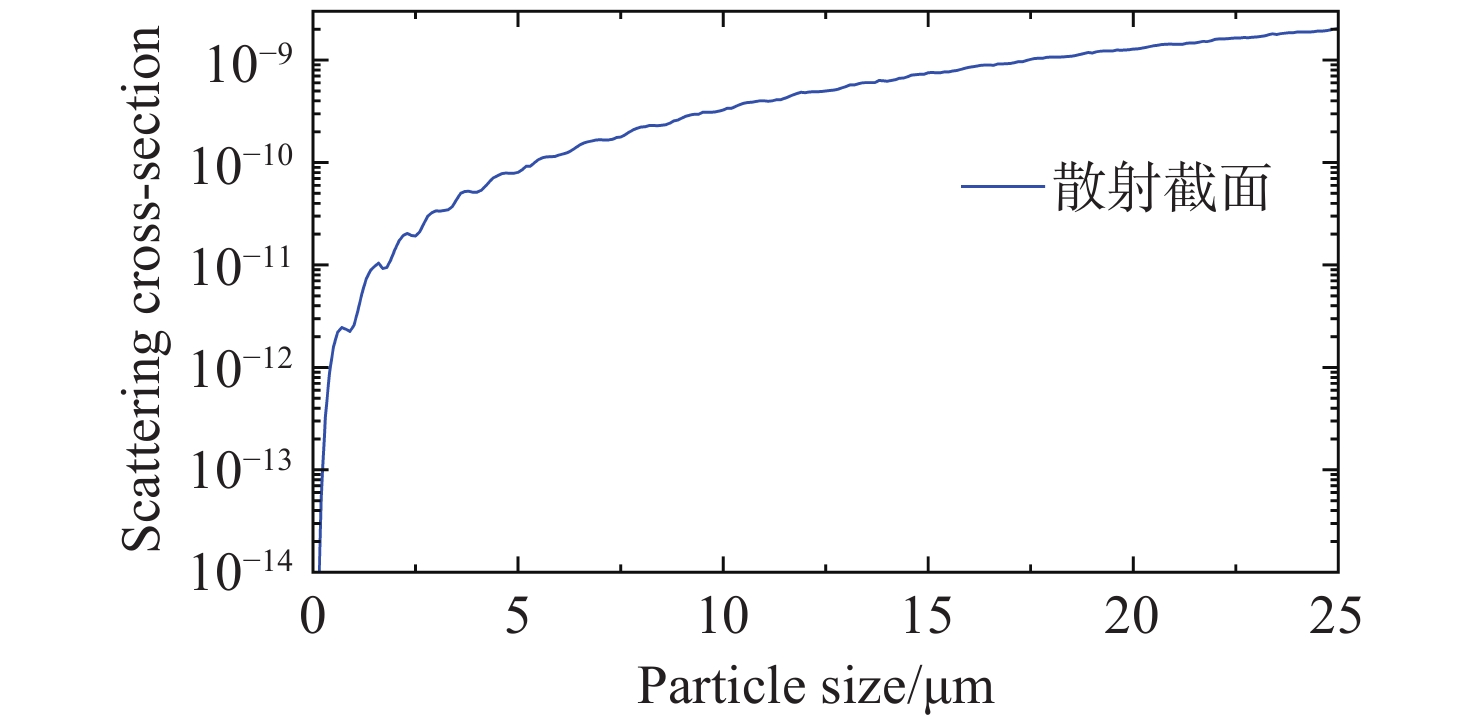
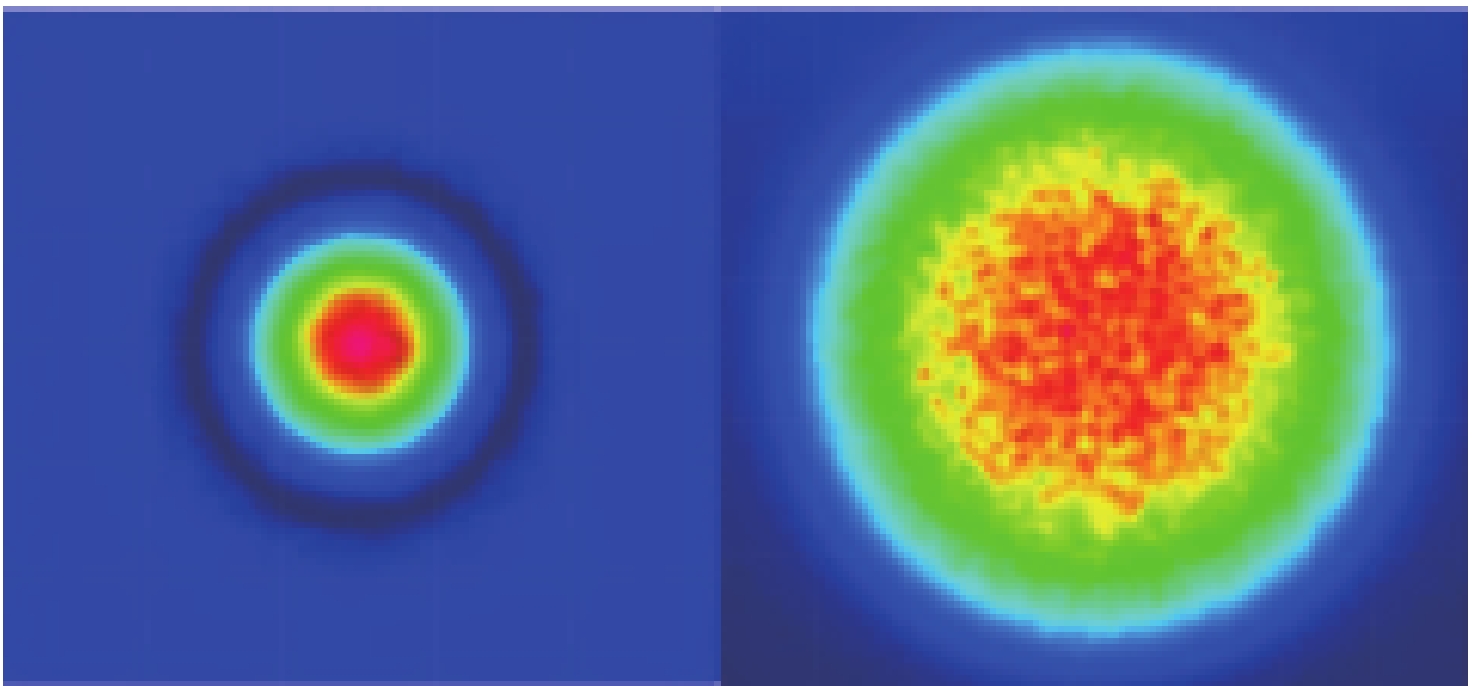
Optical surface particulate contamination detection is critical to maintaining the imaging performance of space telescopes. Conventional approaches typically employ dark-field scattering microscopy to capture particle images, where particle size is estimated from the circumcircle of the particle’s contour. However, this method requires precise focusing during image acquisition and is prone to large errors when dealing with irregularly shaped particles. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a novel sizing method based on defocus-induced blur circles. By exploiting the relationship between particle size and its scattered light energy, the defocused dark-field scattering image of a particle is transformed into a blur circle, whose properties can be analyzed to determine the actual particle size. Unlike conventional contour-based measurements, the blur-circle approach is inherently less sensitive to particle shape irregularities and system defocus. Experimental validation demonstrates that the proposed method achieves high sizing accuracy across varying defocus distances. Compared with traditional dark-field scattering microscopy, the average measurement error for irregularly shaped particles is significantly reduced from 58% to 10.3%. These results confirm both the feasibility and effectiveness of the blur circle method in improving measurement precision for irregular particulate contaminants.
Laser cleaning technology, as an efficient and environmentally friendly surface treatment method, plays significant application potential in the field of chip packaging molds cleaning. This research systematically investigated the effects of laser parameters (pulse duration, repetition rate, average power) on the cleaning effect of Epoxy Molding Compound (EMC) contaminates from mold surface coated with chromium on P20 alloy and ASP23 alloy substrates. The experiment employed a
In order to find out performance of the C-point dipole nested in partially coherent stochastic vortex beam in oceanic turbulence, the Gaussian-Schell model vortex (GSMV) beam carrying a C-point dipole is constructed, which is used to research the evolution property of the C-point dipole in oceanic turbulence. According to the definition of the polarization singularities in partially coherent vector beams, the GSMV beam was constructed to realize a partially coherent beam carrying a pair of C-point dipoles with opposite topological charges. According to the extended Huygens–Fresnel principle, the formula of the cross-spectral density (CSD) for the GSMV beam propagating through oceanic turbulence is deduced by using of the integral formula. In accordance with the formula of the CSD derived above, the effects of propagation distance
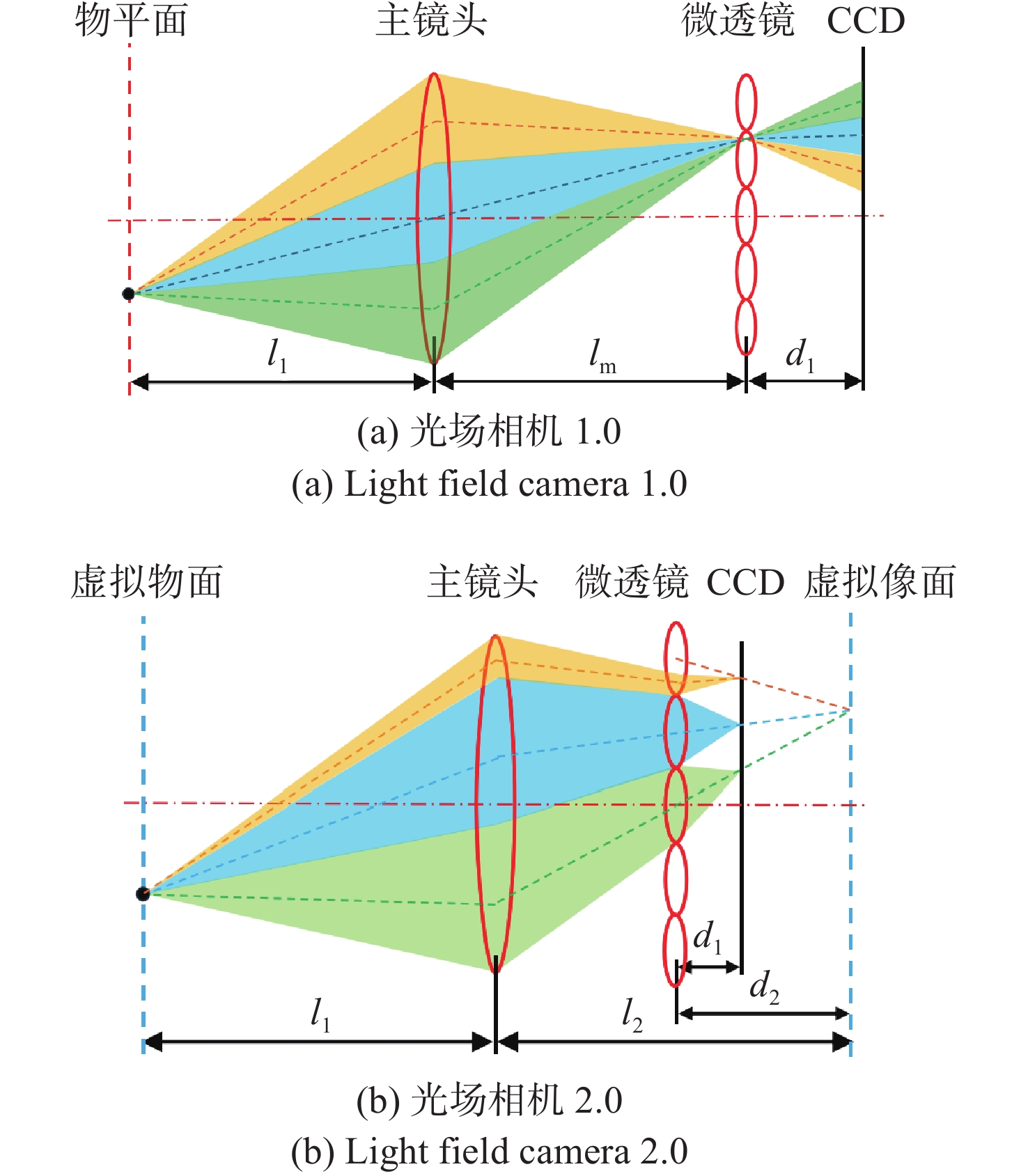
In the process of 3D scene reconstruction, the spatial resolution of the light field camera (LFC) affects the recoverable spatial details as well as the depth resolution, thereby influencing the accuracy of the 3D reconstruction. Therefore, calculating and analyzing the spatial resolution of the LFC is crucial for identifying the high and low resolution regions. In this paper, a calculation method for the spatial resolution of an LFC is explored based on the forward ray-tracing technique, which has the advantage of high accuracy. The spatial resolutions of LFC 1.0 and LFC 2.0 under different microlens array configurations are quantitatively calculated and compared. In addition, the effects of the inverse magnification (
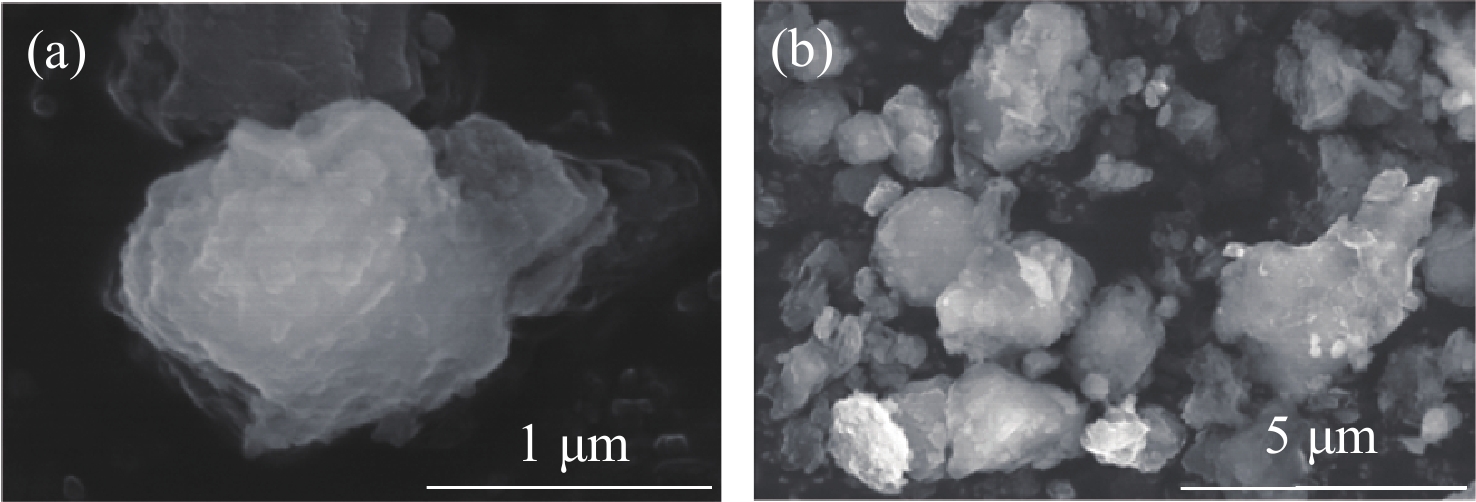
To accurately quantify the attenuation of visible light in urban optoelectronic systems during dust weather, we establish a predictive model that integrates corrections for non-spherical particles, using the Hohhot region as a case study. Utilizing Mie scattering theory alongside scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy data from local dust samples, the extinction characteristics of dust particles in typical red green and blue wavebands were calculated. Scattering parameters for non-spherical particles were corrected via the T-matrix method. Photon multiple scattering was then simulated with the Monte Carlo method to systematically compare attenuation rates between single and multiple scattering models. The results demonstrate that the single-scattering model systematically overestimates the attenuation rate, with a maximum error of 18.3% in the blue band. After multiple scattering correction, the attenuation rate decreased by an average of 12.4%. In this case, when the visibility is 400 meters, the attenuation rate for blue light was approximately 95 dB/km, significantly exceeding the value of 70 dB/km for red light. The hybrid model developed significantly enhances the prediction accuracy for visible light attenuation in dusty environments, elucidating the critical roles of multiple scattering effects. This work provides a reliable theoretical and data-driven foundation for optimizing urban optoelectronic systems in dust-prone conditions.
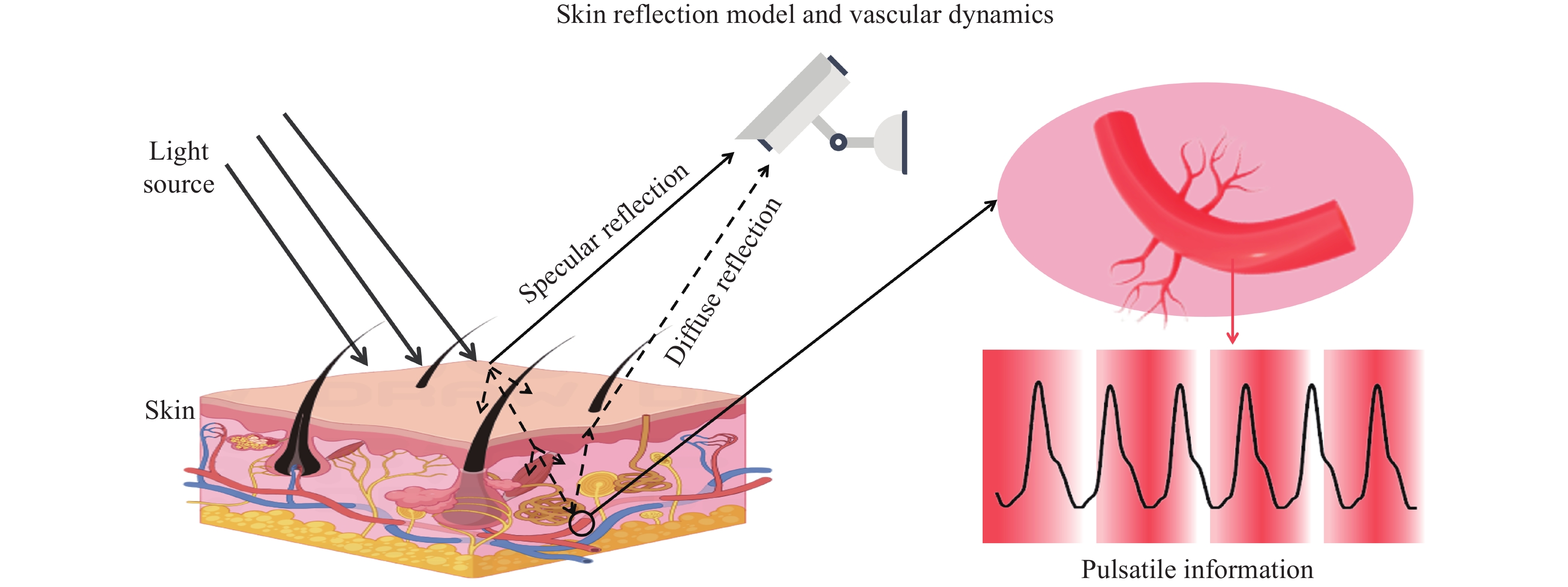
Image Photoplethysmography (IPPG) signals are easily disturbed by noise during acquisition. To address the issue, this study proposes a denoising diffusion probability model for IPPG (DDPM-IPPG). This model eliminates baseline drift and noise through diffusion and reverse diffusion stages, and improves the signal-to-noise ratio and heart rate accuracy. First, Gaussian noise is gradually added to the photoplethysmography (PPG) signal during the diffusion phase to create a noise sequence. A noise predictor based on a nonlinear fusion module and a bridging module is trained. Subsequently, in the reverse diffusion phase, the well-trained noise predictor is employed to perform step-by-step denoising on the initially extracted IPPG signal. Through this denoising, a signal with high signal-to-noise ratio is recovered. The model proposed in this paper is validated and compared with current mainstream algorithms on the PURE, UBFC-IPPG, UBFC-Phys, and MMPD datasets. The experimental results show that DDPM-IPPG improves the signal-to-noise ratio by 1.06 dB on the PURE dataset comparing with the existing highest-precision extraction method. The mean absolute error of heart rate decreases by 0.24 bpm. The root mean square error of heart rate decreases by 0.41 bpm. On the UBFC-IPPG dataset, the signal-to-noise ratio is improved by 1.50 dB. The proposed DDPM-IPPG model has achieved the current advanced level in eliminating baseline drift and noise from IPPG signals, enabling a more precise approximation of the true signals and providing a more reliable data foundation for physiological health assessment and telemedicine monitoring.
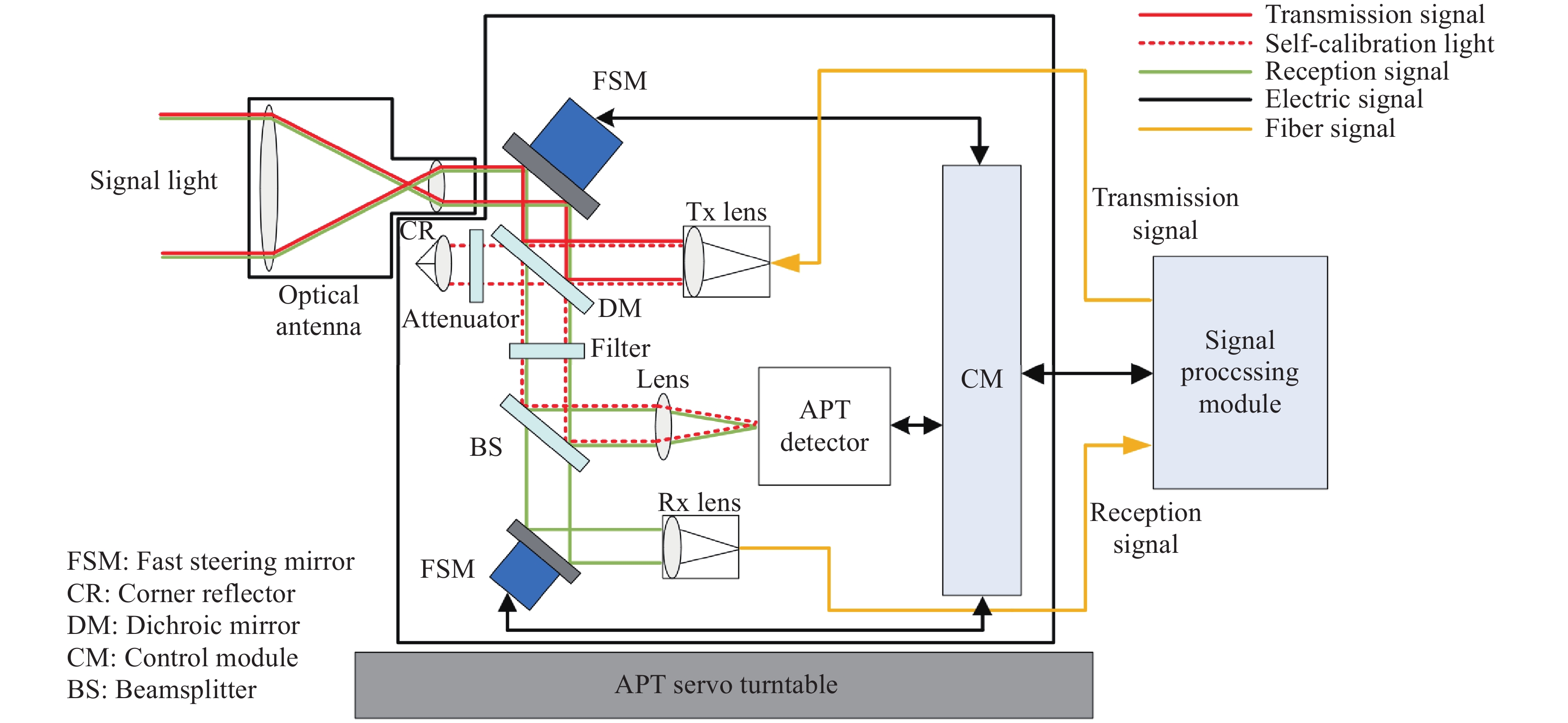
With the rapid development of space laser communication technology, the demand for high-speed inter-satellite networking has been growing significantly. However, existing research on inter-satellite laser communication payload is still primarily experimental, featuring complex optical system designs that require lengthy and costly processes for manufacturing, alignment, and testing-posing challenges for low-cost and rapid mass production. To address this issue, a transmissive optical antenna with single-band achromatic design is proposed in this paper, along with a rapid alignment method for measuring the magnification of the optical antenna based on a collimator. By narrowing the chromatic aberration correction range, the length of the optical antenna is reduced by 15.83%, the number of lenses is decreased from six to four, and the manufacturing cost of a single optical antenna is reduced. Simulation results indicate that the alignment tolerance range for magnification is 4.37 to 5.08. After actual alignment, the measured magnification is 4.82, with a beam divergence of 67.53 μrad on the transmission path and a coupling efficiency of 51.42% on the receiving path. The self-calibration spot size is within 12×12 pixels. A comparative experiment is also conducted, and the proposed method demonstrates a noticeably shorter alignment time than the interferometer method. The alignment and testing results demonstrate that the proposed method not only enables a lightweight and compact design of the optical antenna, but also significantly reduces the alignment time. Simultaneous focal alignment of signal transmission, acquisition-pointing-tracking, and self-calibration optical paths is also achieved.
To achieve high-power and high-beam-quality laser output from a laser-diode (LD) side-pumped solid-state laser, we investigate an unstable resonator incorporating a Gaussian output mirror. The boundary finite element method was utilized to analyze the effects of the resonant cavity length, Gaussian mirror membrane spot radius, and curvature radius on high-order mode suppression. The functional theory of mode loss difference was applied to determine the mode-matching range and the optimal parameters for the spot radius. Furthermore, an output power model was established to derive the theoretical optimal central transmittance for compensating loss. Based on the theoretical and simulation results, the resonator parameters were optimized, and the output beam’s mode distribution and quality were experimentally characterized using different Gaussian mirrors. Under the operational conditions of a 400 mm resonator length, 7.3 A pump current, and 100 Hz repetition frequency, the implementation of a Gaussian mirror with a 3 mm spot radius, 1.5 m curvature radius, and 17% central transmittance produced a high-quality
Multi-band infrared detectors can simultaneously capture radiation information across multiple wavelengths, offering significant advantages over single-band infrared detectors in target recognition, classification, temperature measurement, and information extraction. Consequently, they have become a central focus of infrared detector technology research. As a key optical component of multi-band infrared detectors, the performance of the three-band large-aperture wide-angle infrared mirror directly determines detection accuracy. In the design phase, this study selected three materials: Ge, ZnS, and YbF3, and fabricated a structurally robust infrared reflector coating system through spectral superposition combined with TFCalc software according to high-reflectivity coating design principles. During the preparation stage, ion-source-assisted deposition was employed, and the issue of film delamination was resolved by optimizing the deposition process. During spectral testing, problems related to spectral drift in the samples were addressed through film thickness error experiments and optimization of the YbF3 process. Test results indicate that, at an incident angle of 45°, the infrared mirror achieves an average reflectance of 96.93% in the 3−5 µm spectral band, 96.54% in the 8−12 µm spectral band, and 94.64% in the 1.064 µm spectral band; the spectral non-uniformity within the 270 mm×270 mm aperture for the 3−5 µm and 8−12 µm spectral bands is 4.83%. In accordance with the national standard GJB 2485A-2019 (Environmental Test Standard), the prepared samples successfully passed adhesion and high and low temperature tests, meeting the application requirements for multi-band infrared detectors.
In wide-temperature-range applications, traditional optical systems often struggle to maintain stable imaging quality, primarily because conventional athermal design methods fail to fully account for the differences in the linear expansion coefficients and refractive index temperature coefficient of glass materials at high and low temperatures. To address this issue, this paper proposes an athermal design method for wide temperature ranges. By reconstructing the thermal aberration modeling process, the method accurately characterizes the nonlinear response of thermal aberrations to temperature variation, thereby selecting glass material combinations that minimize the overall thermal optical power within the wide temperature range. In combination with the thermal expansion properties of the housing material, it effectively suppresses system focal shift. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, an optical system with a focal length of 100 mm, an F-number of 2.2, and a field of view of 7° was designed. Simulation results show that within the temperature range of −30°C to 270°C, the system consistently maintains high imaging performance. The modulation transfer function (MTF) remains above 0.5 at 56 lp/mm across all fields and temperatures. The spot diameter is less than 9 μm, and more than 90% of the energy is enclosed within an 18 μm circle. The above results fully verify the effectiveness of the proposed method and provide strong support for athermal design of optical systems under wide temperature ranges. Meanwhile, the method demonstrates good engineering adaptability and shows broad application prospects in the design of imaging systems for complex environments.
Off-axis reflective optical systems are widely employed in Earth observation and mapping owing to their advantages of wide field of view (FOV), high image quality, and stable interior orientation elements. To address the degraded off-axis image quality and thermally induced pointing drift of initial designs from conventional aberration-cancellation methods, this study analytically derives the third-order aberration coefficients of a three-mirror system, assuming a stop at the secondary mirror and symmetric axial spacing between the primary and tertiary mirrors. To further enhance imaging performance, fourth-order aspheric terms are introduced on both the primary and tertiary mirrors, thereby increasing the degrees of freedom for optimization. A comprehensive image-quality evaluation function incorporating quasi-telecentric constraints is constructed, and a hybrid genetic algorithm-sequential quadratic programming (GA-SQP) approach is employed to obtain an optimized initial configuration. The resulting system achieves a focal length of 260 mm, an F-number of 10, and a 7° × 30° FOV, with a modulation transfer function (MTF) above 0.25 at 77 lp/mm, a maximum distortion of 2%, and a maximum chief-ray angle of 2.3°. Microcrystalline glass and titanium alloy are adopted as the mirror substrate and structural materials, respectively. Finite-element thermal analysis is performed under a 6.8 °C temperature gradient, and the optical axis rotation, evaluated using the TRIAD algorithm, is −1.3″ around the
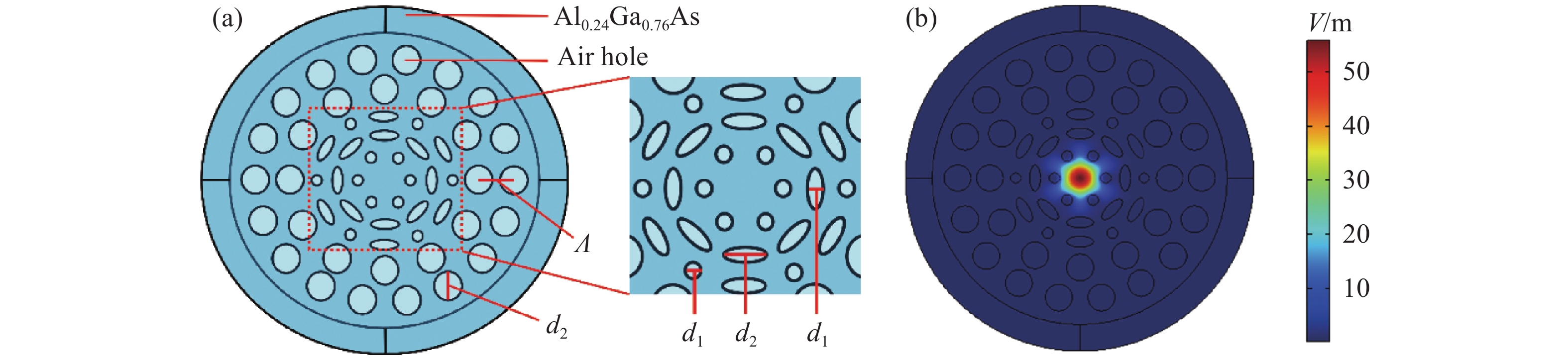
An alternative elliptical and circle air-hole-assisted Al0.24Ga0.76As photonic crystal fiber (PCF) was proposed for generating broadband high-coherence mid-infrared supercontinuum, and the dispersion, effective mode area and nonlinear coefficient were investigated by using finite element method (FEM), the evolution of optical pulses propagating along the fiber was simulated, and the supercontinuum and the coherence were analyzed and evaluated under different pumping conditions. The results show that a supercontinuum spectrum with a spectral width of 4.852 μm can be obtained in the proposed fiber with
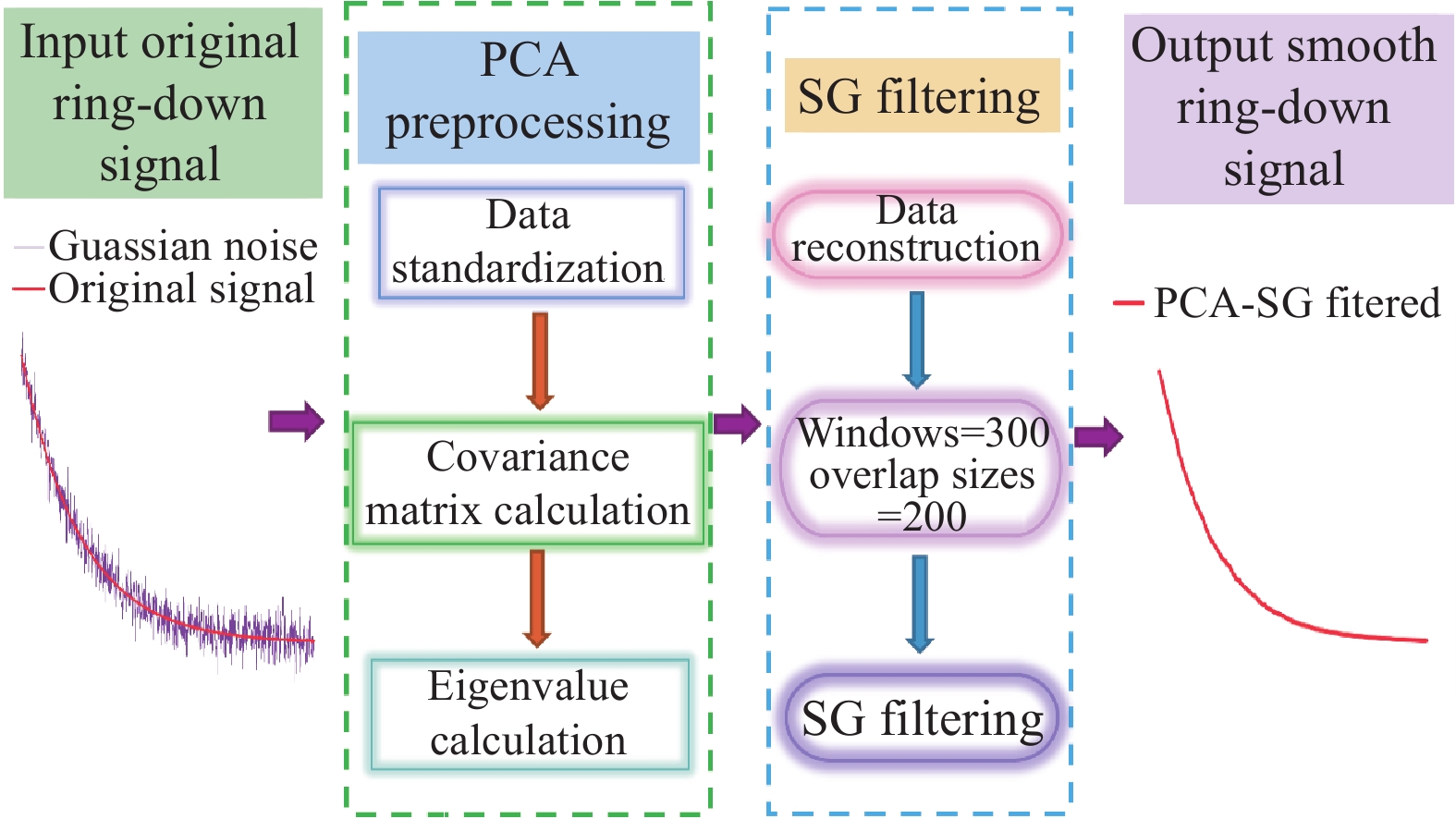
The Savitzky-Golay (SG) filter, which employs polynomial least-squares approximations to smooth data and estimate derivatives, is widely used for processing noisy data. However, noise suppression by the SG filter is recognized to be limited at data boundaries and high frequencies, which can significantly reduce the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). To solve this problem, a novel method synergistically integrating Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with SG filtering is proposed in this paper. This approach avoids the issue of excessive smoothing associated with larger window sizes. The proposed PCA-SG filtering algorithm was applied to a CO gas sensing system based on Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy (CRDS). The performance of the PCA-SG filtering algorithm is demonstrated through comparison with Moving Average Filtering (MAF), Wavelet Transformation (WT), Kalman Filtering (KF), and the SG filter. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm exhibits superior noise reduction capabilities compared to the other algorithms evaluated. The SNR of the ring-down signal was improved from
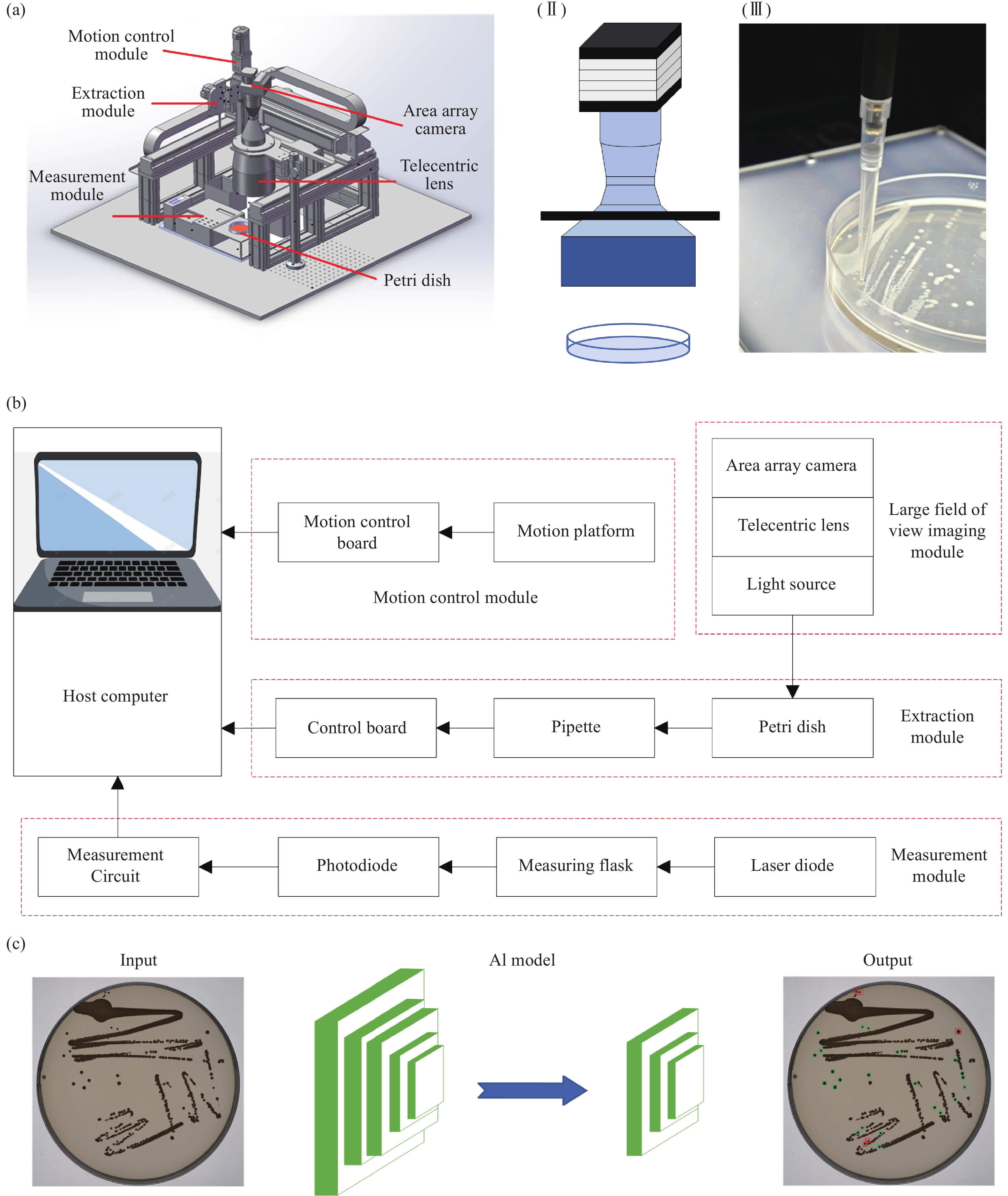
Standard bacterial suspensions play a crucial role in microbiological diagnosis. Traditional preparation methods, which rely heavily on manual operations, face challenges such as poor reproducibility, low efficiency, and biosafety concerns. In this study, we propose a high-precision automated colony extraction and separation system that combines large-field imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) to facilitate intelligent screening and localization of colonies. Firstly, a large-field imaging system was developed to capture high-resolution images of 90 mm Petri dishes, achieving a physical resolution of 13.2 μm and an imaging speed of 13 frames per second. Subsequently, AI technology was employed for the automatic recognition and localization of colonies, enabling the selection of target colonies with diameters ranging from 1.9 to 2.3 mm. Next, a three-axis motion control platform was designed, accompanied by a path planning algorithm for the efficient extraction of colonies. An electronic pipette was employed for accurate colony collection. Additionally, a bacterial suspension concentration measurement module was developed, incorporating a 650 nm laser diode as the light source, achieving a measurement accuracy of 0.01 McFarland concentration (MCF). Finally, the system’s performance was validated through the preparation of an Esckerichia coli (E. coli) suspension. After 17 hours of cultivation, E. coli was extracted four times, achieving the target concentration set by the system. This work is expected to enable rapid and accurate microbial sample preparation, significantly reducing detection cycles and alleviating the workload of healthcare personnel.
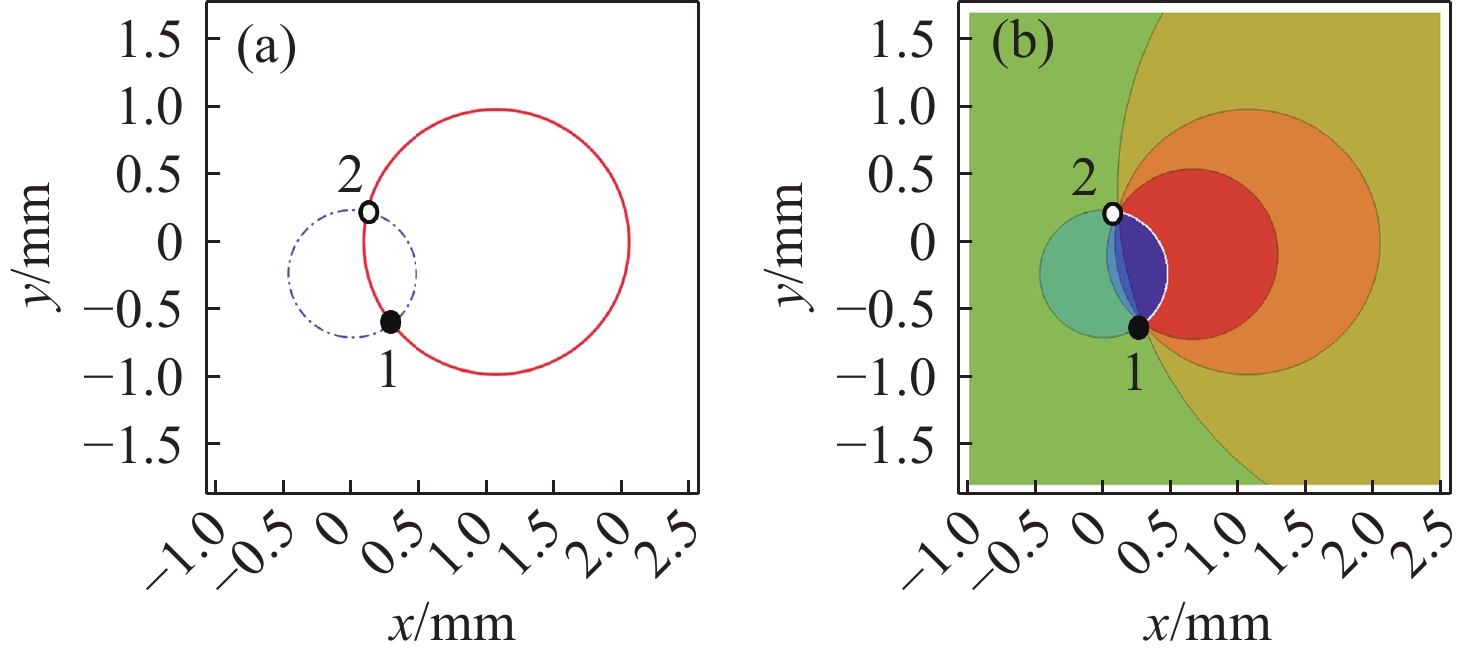
Due to the inability of manufacturing a single monolithic mirror at the 10-meter scales, segmented mirrors have become indispensable tools in modern astronomical research. However, to match the imaging performance of the monolithic counterpart, the sub-mirrors must maintain precise co-phasing. Piston error critically degrades segmented mirror imaging quality, necessitating efficient and precise detection. To address the limitations that the conventional circular-aperture diffraction with two-wavelength algorithm is susceptible to decentration errors, and the traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) struggle to capture global features under large-range piston errors due to their restricted local receptive fields, this paper proposes a method that integrates extended Young’s interference principles with a Vision Transformer (ViT) to detect piston error. By suppressing decentration error interference through two symmetrically arranged apertures and extending the measurement range to ± 7.95 μm via a two-wavelength (589 nm/600 nm) algorithm. This approach exploits ViT’s self-attention mechanism to model global characteristics of interference fringes. Unlike CNNs constrained by local convolutional kernels, the ViT significantly improves sensitivity to interferogram periodicity. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a measurement accuracy of 5 nm (
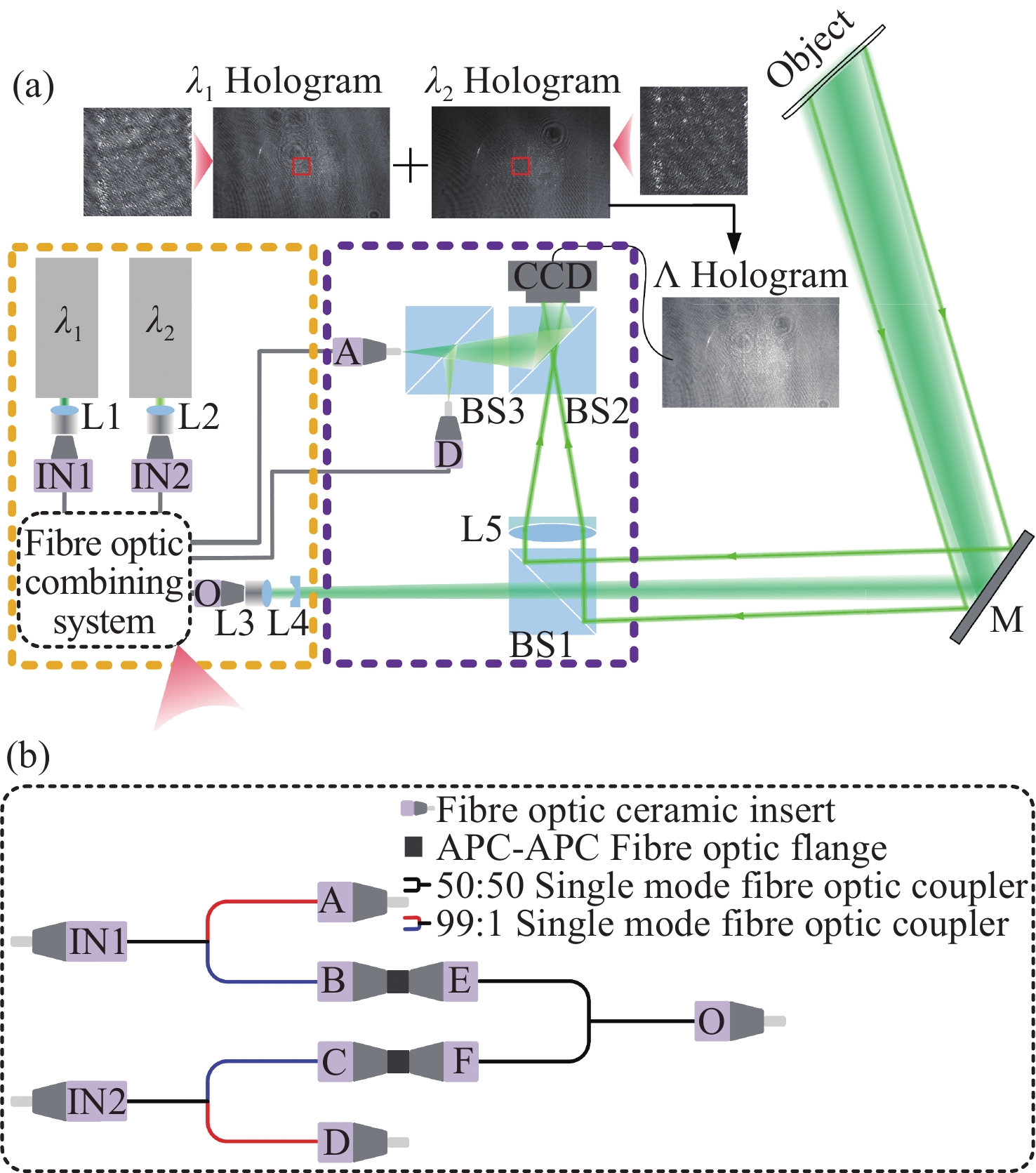
The dual-wavelength image plane digital holography is employed to achieve the long-distance topography measurements, which is expected for the Examination and Analysis System Technology (EAST) in divertor surface monitoring. The same-path design for the illumination and imaging beams is suitable for the upper diagnosis channel of the tokamak device. By selecting two wavelengths with a gap of 1.02 nm, the measurement range of system is extended to 276.87 µm, allowing for 138.44 µm gradient measurements. Experimental results demonstrate that the measurement error of the system for a step with a nominal high of 80 μm is 7.00%, with a minimum detectable height variation of 10 μm. Furthermore, the long-distance measurement capability of the system was confirmed, and off-line measurements were conducted on a dismantled divertor from a tokamak device, proving that the system can be applied to the topography measurements of the divertor.
In recent years, the demand for synchronous acquisition of three-dimensional (3D) shape and color texture has surged in fields such as cultural heritage preservation and healthcare. Addressing this need, this paper proposes a novel method for simultaneous 3D shape and color texture capture. First, a linear model correlating camera exposure time with grayscale values is established. Through exposure time calibration, the projected red, green and blue (RGB) light and white-light grayscale values captured by a monochrome camera are aligned. Then, three sets of color fringes are projected onto the object to identify optimal pixels for 3D reconstruction. And, three pure-color patterns are projected to synthesize the color texture. Experimental results show that this method effectively achieves synchronous 3D shape and color texture acquisition, offering high speed and precision, and avoids color crosstalk interference common in 3D reconstruction of colored objects using a monochrome camera.
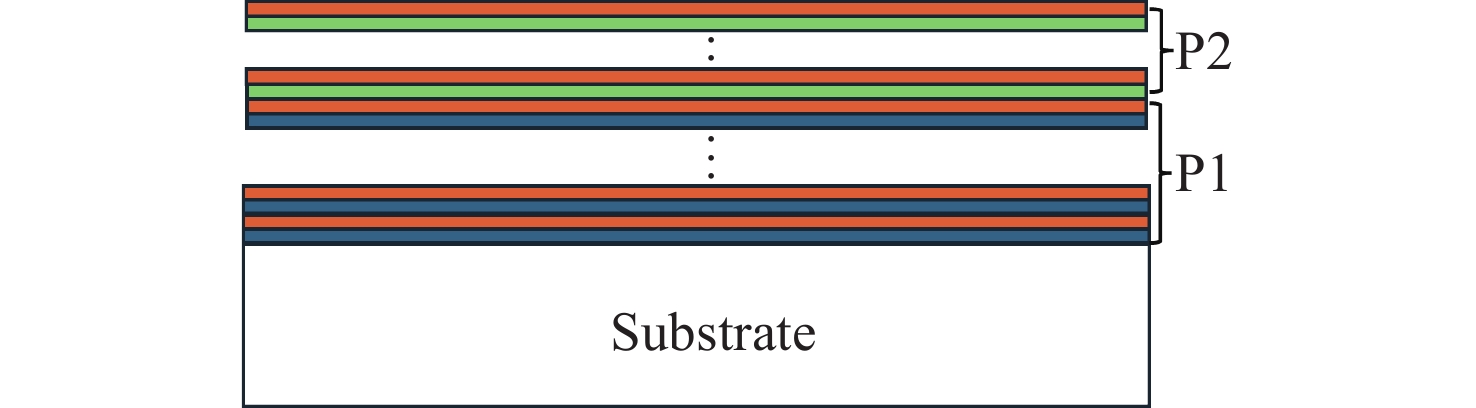
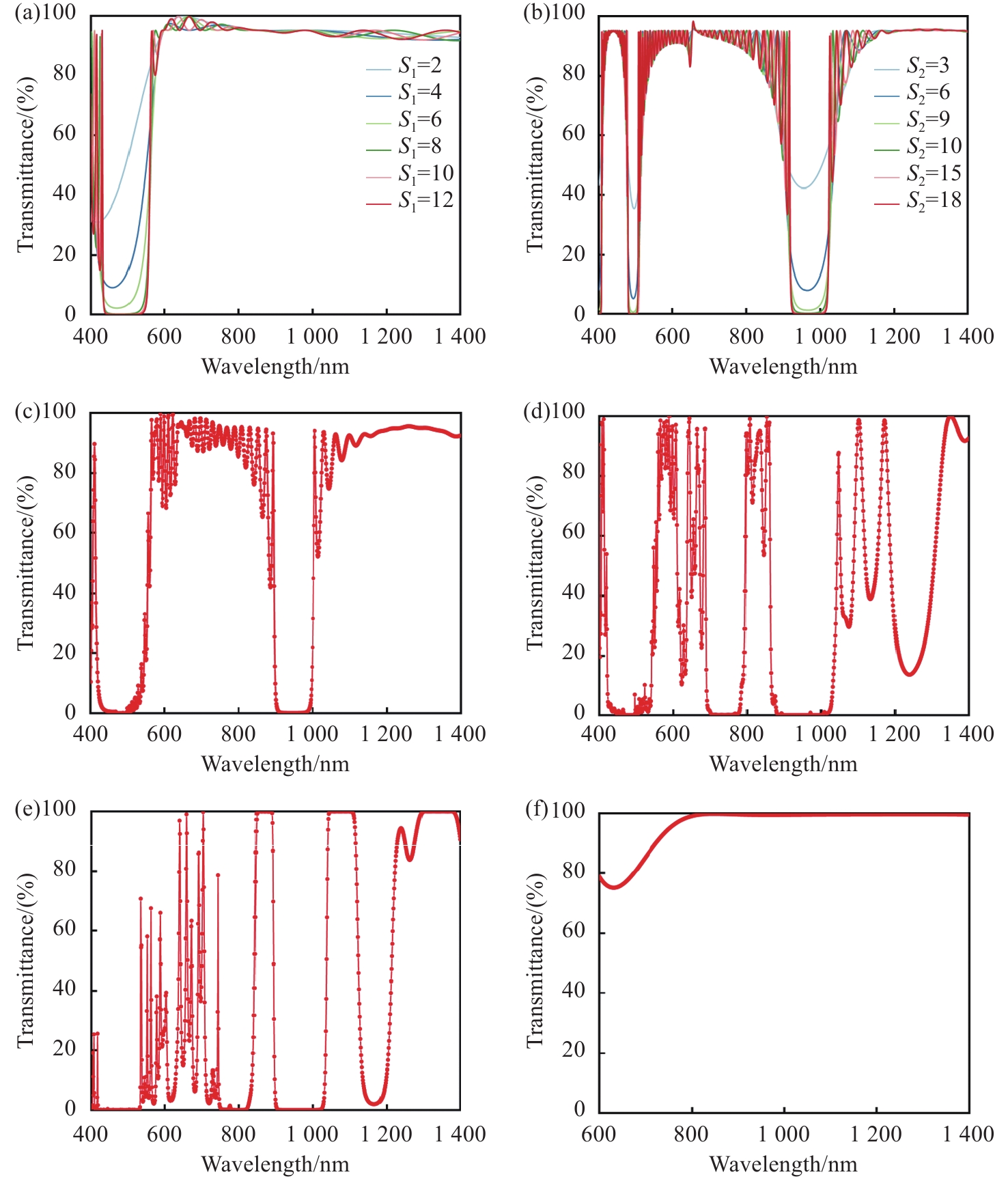
Filters, as a key component in the photoelectric detection system, can simplify the optical system and improve detection efficiency. Based on the usage requirements, a visible/near-infrared filter film with up to 5 wavebands needs to be designed and prepared, while simultaneously satisfying high reflection in 2 wavebands and high transmittance in 3 wavebands. Therefore, we have conducted a systematic study on the film design, thin film preparation process, and control accuracy of film layer thickness. In this work, the short-wave pass film system is superimposed with the long-wave pass film system, and the number of cycles and matching coefficient of the film system are tuned to meet the requirements of cut-off band. Additionally, Smith method was used to match bandpass film system to optimize the transmission band and complete the visible/near infrared multiband laser filter film design. In the preparation process, combined with the sensitivity of the film layer, inverse analysis is used to invert the film layer monitored by each optical monitoring chip. The optical control scheme with weak optical signal in the monitoring process is simulated and corrected, and the monitoring wavelength with stronger optical signal is matched, resulting in an improvement of the control accuracy for the film thickness and the transmittance in the specified wavelength range. Ultimately, the actual physical thickness is 9.66 μm, and the error with the theoretical design thickness is less than 0.4%, and the transmittance of the specified 3 wavebands exceeds 99%. The average transmittance of the cut-off bands at the 455−500 nm and 910−


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 2235KB
PDF 2235KB