Latest Articles
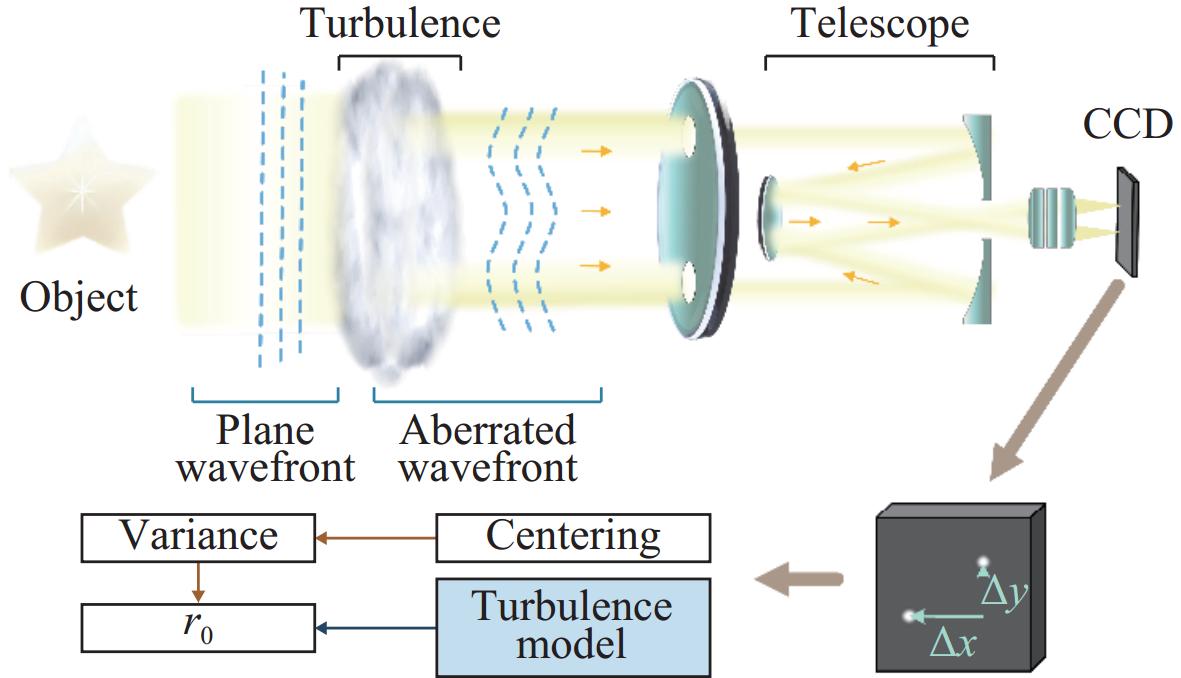
To measure the atmospheric coherence length, an important parameter that characterizes the impact of atmospheric turbulence on the performance of free-space optical communication links, we propose a novel strategy for measuring atmospheric coherence length by taking extended targets as the information source. Specifically, the method integrates the wavefront structure function approach with the extended target offset algorithm to directly estimate the atmospheric coherence length. Traditional methods, such as the Differential Image Motion Monitor (DIMM), typically rely on guide star targets, which are difficult to set appropriately in horizontal communication links, thereby limiting their effectiveness in practical applications. In contrast, employing extended targets as direct detection targets provides a feasible solution for measuring atmospheric coherence length. The paper first reviews the principles and current research status of mainstream algorithms, emphasizing the reliance of existing algorithms on guide star targets and their limitations in horizontal links. Subsequently, we propose a new measurement scheme that combines the improved normalized cross-correlation algorithm with the wavefront structure function method to estimate atmospheric coherence length under extended targets scenarios. In comparison to traditional measurement methods, our approach can realizes coherence length measurement based on extended targets in horizontal links, thereby significantly reducing system complexity and equipment costs. To validate the effectiveness and measurement accuracy of the proposed method, both simulations and experiments were designed and conducted. The results demonstrate that the coherence length values measured by this method are highly consistent with those obtained using the DIMM method and the wavefront phase variance method, with a measurement accuracy error of approximately 4%. This indicates that the proposed method can effectively assess atmospheric coherence length, thereby providing a valuable reference for enhancing the reliability of free-space laser communication systems.
Noise interference critically impairs the stability and data accuracy of sensing systems. However, current suppression strategies fail to concurrently mitigate intrinsic system noise and extrinsic environmental noise. This study introduces a composite denoising approach to address this challenge. This method is based on the ameliorated ellipse fitting algorithm (AEFA) and adaptive successive variational mode decomposition (ASVMD). System noise is closely correlated with the direct-current and alternating-current components in the interferometric signal. AEFA effectively suppresses this noise by removing these components. The ASVMD technique adaptively extracts environmental noise components predominantly present in the phase signal. To achieve optimal decomposition results automatically, the permutation entropy criterion is employed to refine decomposition parameters. The correlation coefficient is utilized to differentiate effective components from noise components in the decomposition results. Experimental results indicate that the combined AEFA and ASVMD algorithm effectively suppresses both system and environmental noise. When applied to 50 Hz vibration signal processing, the proposed approach achieves a noise reduction of 17.81 dB and a phase resolution of 35.14 μrad/√Hz. Given the excellent performance of the noise suppression, the proposed approach holds great application potential in high-performance interferometric sensing systems.
To address the challenge of achieving high-precision registration between visible light (RGB) and photoluminescence (PL) images in Micro LED defect inspection, which arises from substantial modality differences, this study introduces a robust multimodal image registration approach capable of attaining sub-pixel accuracy, aiming to establish a direct mapping between the physical structure and electrical characteristics of the chips. We propose a registration method that integrates structural feature constraints with bidirectional residual optimization. First, leveraging the geometric regularity of Micro LED arrays, a tailored feature detection strategy is employed: electrode centers in RGB images are accurately extracted via ellipse fitting and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN), while chip centers in PL images are localized using an enhanced watershed algorithm with sub-pixel refinement. Second, during the registration optimization stage, a bidirectional residual constraint framework is constructed, incorporating a confidence weighting mechanism derived from residual distribution analysis. The optimal affine transformation parameters are then estimated using an iterative reweighted least squares method. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves sub-pixel-level accuracy, with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.823 pixels, representing a 94.2% reduction compared to baseline methods. The root mean square error (RMSE) is 0.996 pixels, the maximum error remains below 2.839 pixels, and the inlier rate attains 75.0%. Each registration process takes only 0.036 seconds on average, achieving an order-of-magnitude improvement in computational efficiency over traditional mutual information (MI) methods. By effectively mitigating feature mismatch and outlier interference in multimodal images, the proposed method outperforms conventional approaches in terms of registration accuracy, robustness, and efficiency, thereby providing a reliable technical foundation for precise defect detection and multimodal analysis of Micro LED chips.
The structure of multilayer dielectric film will modulate the optical field, thus in the study of laser-induced damage characteristics, it is necessary to consider the energy distribution within the film system and the resulting changes in material optical properties.
Taking the HfO2/SiO2 multilayer dielectric film structure as an example, and based on the laser-induced ionization/electron multiplication process, the Drude model is introduced into the optical field calculation, extending the film layer refractive index from a static constant to a dynamic complex refractive index driven by the free electron density. Based on this, a thermal conduction (and thermal stress) model is coupled to calculate the evolution of thermal effects inside the thin film under nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation, and the corresponding damage threshold is determined to be 13.65 J/cm2, and the damage characteristics of the film are studied experimentally.
The verification experiment observed that the damage appearance of the HfO2/SiO2 multilayer dielectric film is a round hole type, which is a typical thermal melting damage, and is consistent with the conclusion of the theoretical model. The measured damage threshold is 13.75 J/cm2, which is only higher than the theoretical analysis result.
The improved model established is helpful to further analyse the interaction between strong laser and multilayer dielectric film from the theoretical level, and to better study the damage resistance of optical thin film.
To address the challenge of temperature rise control during the coating process for thermally sensitive substrates (e.g., epoxy adhesive-bonded structural components), this paper proposes a low-temperature electron beam evaporation coating process. Through a dynamic thermal management strategy featuring segmented deposition-cooling cycles, the performance of this process in terms of the core properties (i.e., stress, adhesion, and optical performance) of metallic reflective films-with silver films as the research subject-was systematically investigated, and the deposition process was optimized by integrating the thermal failure threshold of the epoxy adhesive. Experimental results demonstrate that under strictly controlled substrate temperature conditions, this process not only significantly reduces the residual stress of the reflective film, but also ensures that the interfacial adhesion meets the strictest Class 03 severity level specified in the national standard (GB/T 26332.4-2015/ISO 9211-4:2012), the average reflectivity in the visible wavelength range is comparable to that of the traditional continuous coating process (>99%@450−900 nm), and the substrate temperature rise remains consistently below the critical threshold of the epoxy adhesive. Through the synergistic effect of Ion-Assisted Deposition (IAD) and dielectric encapsulation, the oxidation resistance and environmental durability of the silver film are significantly improved, satisfying the long-term service requirements of aerospace optical devices under extreme multi-physics field coupled environments. Further theoretical analysis reveals that the thermal relaxation mechanisms and structural regulation principles of this process exhibit cross-scenario applicability, providing an innovative solution for high-performance coating of low-temperature-sensitive substrates that balances aerospace reliability and industrial universality.
To enhance the imaging performance of arthroscopes in clinical surgery and broaden their potential for clinical applications, a wide-spectrum arthroscopic optical system featuring a large field of view, high resolution, and parfocal imaging capability in both visible and near-infrared bands was designed. The objective lens use a high optical power negative lens to compress the chief-ray angle and reduce the optical path difference between off-axis and on-axis rays. Through conjugate aperture imaging, an equivalent virtual stop is formed inside the turning prism, which allows the system to maintain both high transmission efficiency and high image quality under a limited aperture. The relay lens adopts a near-symmetric structure, and by distributing optical power and Abbe numbers appropriately, it effectively suppresses the accumulation of axial chromatic aberration across the broad spectral range, thereby achieving parfocal imaging. Tolerance analysis shows that the system has good manufacturability and assembly feasibility. Experimental results verify that the designed wide-spectrum arthroscope achieves parfocal imaging in the visible and near-infrared bands with a 95° field of view, and angular resolutions of 4.34 C/(°) and 2.74 C/(°), respectively. The optical system provides a feasible solution for achieving low-cost, high-performance fluorescence arthroscopy and has significant application value.
To meet the research requirements of the optical response of micro-area in surface plasmon nanostructures, this paper has develops a micro-area angle-resolved spectroscopy measurement system based on a coaxial rotating arm. The system adopts a micro-area remote excitation and collection optical path model based on a finite conjugate configuration, enabling an incident micro-area spot with a diameter of 32 μm. In addition, an angle-resolved mechanical system based on a coaxial rotating arm is constructed, realizing large-range directional angular excitation from 6.9° to 90°. Performance tests show that the system exhibits high stability, with a minimum angular resolution of 0.12°. Through the reflection spectrum collection experiments on one-dimensional gratings and two-dimensional periodic nanostructures, the reliability of the system is further verified. The results demonstrate the advantages of the micro-area spot and provide an effective technical means for the angle-resolved spectroscopy characterization of micro and nanostructures.
Objetive: To address the inherent limitations of conventional portable non-mydriatic fundus cameras, including the mutual constraints between illumination and imaging optical paths, severe interference from corneal stray light, and the difficulty of achieving simultaneous clear imaging of different retinal regions, this paper proposes a novel fundus optical system design. Method: The proposed system adopts a four-point rectangular illumination layout combined with regionally adjustable illumination intensity. At a pupil diameter of 3.2 mm, the corneal stray light is reduced by 91.56% compared with traditional approaches, enabling high-contrast synchronous imaging of both the optic disc and macular regions. Furthermore, a separated illumination and imaging optical path architecture is employed. By integrating a wire-grid polarizer with a stacked liquid-crystal polarization scheme, stray light caused by optical surface reflections is effectively suppressed. Result: Within a compact system envelope of 230.4 mm × 90 mm, the proposed fundus camera simultaneously achieves a wide field of view of 53°, a refractive error compensation range of ±20 D, and a retinal spatial resolution of 6 μm. Conclusion: The proposed system enables the acquisition of high-contrast retinal images with clearly resolved details of both the optic disc and macula in a single-shot capture, demonstrating its suitability for portable non-mydriatic fundus imaging applications.
To address the issues of structural complexity and high cost in high-performance optical systems, this study proposes an optical system simplification and aberration correction method oriented toward computational correction. On the optical design side, a simplification design criterion based on aberration correctability analysis is constructed: priority is given to suppressing aberrations that are difficult for neural networks to compensate, while retaining portions amenable to computational correction, thereby simplifying the optical system structure while ensuring imaging quality. On the computational processing side, a multi-module progressive collaborative correction network is designed, comprising four modules: distortion correction, chromatic aberration compensation, monochromatic aberration correction based on physically-constrained Point Spread Function, and frequency-domain enhancement. This network is driven by a Temporal Stage Controller (TSC), which utilizes its dynamic weight scheduling mechanism for progressive stage-wise processing, effectively suppressing the mutual interference between different aberration types. Experimental results demonstrate that images from a simplified dual-lens system corrected by this network achieve a Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) of 31.47 dB and Structural Similarity (SSIM) of 0.95, with imaging quality comparable to conventional six-lens double-Gauss systems, while significantly reducing optical system complexity. Ablation studies validate the effectiveness of the TSC and multi-module correction architecture. This research provides a novel technical pathway for achieving high-quality imaging with simplified optical systems.
This paper presents comprehensive theoretical and experimental investigations on the transmission spectral characteristics of an integrated photonic structure consisting of a microring resonator coupled with a Fabry–Perot (FP) cavity. The FP cavity is realized by introducing a grating reflector into the straight waveguide of a single-side-coupled microring. Within this dual-resonator configuration, novel multi-cavity coupled transmission spectra are achieved. A systematic theoretical model is established to analyze the conditions under which these multi-cavity coupled spectral profiles appear, and the structural parameters are subsequently optimized. A grating-type Fabry–Perot–microring coupled resonator device was successfully fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) platform. For the first time, multi-cavity coupled transmission spectra consistent with theoretical predictions were experimentally observed, including nested electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like and double Fano resonance line shapes. Experimental measurements indicate that, under a waveguide loss of 3.43 dB/cm, the EIT central peak exhibits a quality factor of 1.40×104, while the slope of the double Fano resonance reaches 37.70 dB/nm. These results provide new insight into the underlying mechanisms of integrated photonic coupled resonator systems and demonstrate a viable approach toward highly integrated, high-performance photonic device platforms. The proposed structure shows strong potential for applications in high-sensitivity optical sensing, narrowband filtering, and high-speed modulation.
To reduce pulse pile-up and improve ionizing particle discrimination efficiency. This study uses a CMOS active pixel sensor to analyze ionizing particle optical responses and propose morphology-based discrimination. Particle response features were compared to reveal gain and integration effects, and discrimination effectiveness was validated. Results show α events differ significantly from β and γ events in pixel count, mean pixel value, rectangularity, convexity, and compactness. β and γ events are similar in pixel count, rectangularity, and convexity, but differ in mean pixel value or compactness. Using pixel count, α events were identified with over 99% accuracy. β and γ events were discriminated by mean pixel value with over 82% accuracy. The results provide a new method and basis for ionizing particle identification in mixed radiation fields. It supports nuclear particle discrimination and noise mitigation, providing new approaches and theoretical guidance.
With the rapid development of short-pulse laser technology, the potential threats to CCD image sensors exhibit new characteristics distinct from those induced by traditional continuous-wave or long-pulse laser. To investigate the mechanisms and principles of interference and damage caused by short-pulse laser of different wavelengths, picosecond laser with wavelengths of
During the ascent of an aircraft to its cruising altitude, the external environmental temperature changes drastically. Simultaneously, the internal stepper motors and bearings continuously generate heat due to the periodic rapid start-stop operations of the scanning mirror turntable in the step-scanning mode. These factors cause a temperature gradient across the turntable, which induces thermal deformation of the mirror surface figure and ultimately degrades the imaging quality of the optical system. To address this issue, an analysis method based on thermal-structural coupling is proposed. First, the thermal balance equation of the scanning mirror turntable was established. Combined with the actual thermal boundary conditions, a finite element analysis (FEA) model was constructed. This model was utilized to optimize the design of the mirror assembly and the adhesive layer by analyzing the relationship between the surface figure and adhesive parameters under complex thermal environments and working conditions. The optimization results show that when the adhesive layer thickness is 1 mm, the mirror achieves the optimal surface figure accuracy with a root-mean-square (RMS) value of 43.54 nm. Furthermore, ground thermal chamber tests were conducted to simulate the temperature variations and operating status during takeoff. The relative error between the experimental measurements and the simulation results is less than 10%. These results verify that the proposed method is effective for evaluating the dynamic response characteristics of the scanning mirror surface in a temperature gradient field, providing theoretical support for the design of the mirror bonding layer and related components.
Toward the application demand for high-power, high-beam-quality CO2 seed lasers in extreme ultraviolet lithography light sources, the amplification characteristics were investigated based on a RF waveguide architecture. The static insertion loss and output beam quality of the RF waveguide amplifier were measured as function of incident beam parameters. A numerical model was developed to simulate the multi-stage RF waveguide amplification and to evaluate the effects of the gas pressure and the discharge pumping power on gain. The technology of regulating with gain medium was implemented to optimize the amplification performance in the experiment. Experimentally, optimal mode-matching conditions were identified with a waveguide length of 2.5 m, yielding a transmission efficiency of 91.4%. The beam quality factors of the output beam in the horizontal and vertical directions were 1.03 and 1.05, respectively. An overall gain factor of 68× was achieved in a dual-stage RF waveguide amplifier. The system delivered CO2 laser emission with a repetition rate of 50 kHz, a pulse duration of 20 ns, and an average output power of 17.1 W, satisfying the design criteria and demonstrating its suitability for high-power, high-beam-quality seed laser applications.
The transmission characteristics of rotationally symmetric power-exponent-phase vortex beams (RSPEPVBs) in biological tissues are explored in this study. Based on the extended Huygens-Fresnel principle, a general expression describing the transmission of RSPEPVBs through biological tissues is established. Numerical simulations are performed to explore the influence of the propagation distance
In response to the current demand for high-precision planar displacement measurements in advanced manufacturing equipment, this paper proposes an xz dual-axis grating interferometer. The system adopts a biaxial Littrow incident light path structure, established using a biaxial beam splitter mirror and right-angled prism mirror. The relationship between the parallelism of the outgoing beam, the beam spacing, and the position and angle of the incident light is analyzed. Experimental results verify the feasibility and measurement performance of the proposed interferometer. The grating interferometer achieves a displacement resolution of 5 nm along the x-axis and 7 nm along the z-axis. After correction using the Heydemann algorithm, the periodic nonlinear error is reduced to ±5 nm. Over a travel range of 10 mm, the measurement accuracies are ±30 nm along the x-axis and ±100 nm along the z-axis, respectively. Finally, the influence of the surface error introduced by the non-coincident incident structure on the measurement results is discussed.
This paper presents a high-precision temperature sensor based on a high-quality factor thin-film lithium niobate microring resonator integrated with a microwave photonic readout system. The microring resonator, with a narrow linewidth of 2.87 pm and a high Q-factor of 105, functions simultaneously as the temperature-sensing element and the core signal processing component of a microwave photonic filter. Through the thermo-optic effect, temperature variations are converted into shifts in the optical resonance wavelength, which are innovatively mapped to linear changes in the passband center frequency of the microwave photonic filter. A vector network analyzer is employed to accurately detect the microwave frequency response, enabling temperature measurement via high-resolution frequency variations and establishing a quantitative model between temperature and frequency shift. In contrast to conventional methods that directly track optical wavelength shifts, the proposed microwave photonic readout technique linearly converts minute resonance wavelength shifts into changes in the microwave center frequency, thereby overcoming the resolution limitations inherent in conventional optical spectrum analyzers. Experimental results demonstrate a sensitivity of 27 MHz/°C and a resolution of 0.002 °C, with excellent linearity maintained under temperature variations as small as 0.01 °C. This work effectively resolves the trade-off between sensitivity and resolution in traditional optical temperature sensing, offering a novel solution for on-chip integrated high-precision temperature monitoring.
To achieve uniform heat flux distribution on the receiver surface, an optimization method for heliostat aiming strategy in solar power tower plants is proposed. First, the heliostat field is divided into zones based on the calculated instantaneous optical efficiency of heliostats throughout the entire field, with different aiming factors designed for heliostats in different zones. Then, the spot size of each heliostat is calculated according to the aiming factor, and the relative spot size is determined by the ratio of spot size to receiver size, thereby planning the aiming point distribution. Finally, a genetic algorithm is employed to optimize the heliostat aiming point distribution, achieving uniform heat flux distribution on the receiver surface. Taking a hundred-megawatt-scale solar power tower plant as an example, the heliostat aiming strategy is optimized. Under typical spring equinox conditions, the peak heat flux density on the receiver surface is reduced from 1.94 MW/m2 with equatorial aiming to 1.01 MW/m2, improving uniformity by 53.29% while reducing the spillage factor by 0.86%. This ensures efficient and safe operation of the receiver while maintaining high interception efficiency.
To achieve precise quantification of slag adhesion and process optimization in laser cutting, this study investigates a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based prediction method that integrates both image and frequency-domain features. A dataset of
Aiming at the technical challenge that high resolution and miniaturization are difficult to be reconciled in traditional echelle spectrometers, this paper presents a novel optical design for a compact echelle spectrometer.
First, based on the crossed Czerny-Turner structure, the design adopts a transmission prism as the cross-dispersing element to separate spectra of different orders and a reverse off-axis parabolic focusing mirror mainly for eliminating the aberrations introduced by the prism, thereby realizing the miniaturization of the spatial layout. In this paper, we briefly describe the design methods of echelle gratings and dispersive prisms. Additionally, the aberration characteristics of the focusing optical path is analyzed through the theory of optical path aberration.
The simulation results show that the parabolic-prism type echelle spectrometer has a spectral range of 450~650 nm, a numerical aperture of 0.05, and a resolution up to 0.06 nm. Moreover, under the condition of reasonable tolerance range, the system volume is only 80 mm × 44 mm × 18 mm.
It can satisfy the application requirements of portable and high-precision spectral detection.
Extending the operational wavelength range of integrated optical devices to cover the entire visible spectrum holds significant importance, as it can enhance the detection accuracy and applicability of miniaturized spectrometers, broaden the bandwidth of visible light communication, and enable biosensors to simultaneously detect multiple biomolecules in complex samples. As the fundamental building block of integrated optical devices, waveguides have not yet been thoroughly investigated for full visible spectrum operation. This work presents a waveguide design supporting the full visible spectrum (435−760 nm). Numerical simulations were employed to analyze the transmission characteristics of various waveguide structures, revealing that single-mode propagation cannot be achieved across the entire visible spectrum. Under multimode propagation conditions, key parameters such as propagation loss and mode distribution were systematically examined to determine the optimal waveguide dimensions, bending radii, and waveguide spacings for low-loss transmission: For slab waveguides, a thickness ≥1 μm ensures polarization insensitivity. For strip waveguides with a thickness of 1 μm, a width ≥2 μm significantly reduces scattering loss induced by sidewall roughness. For strip waveguides with a width of 1 μm and thickness of 2 μm, radiation loss becomes negligible when the bending radius ≥10 μm and waveguide spacing ≥0.4 μm, while maintaining effective isolation from adjacent waveguides. Additionally, the impact of fabrication tolerances on waveguide performance was evaluated. In contrast to previous studies primarily focusing on narrow spectral bands within the visible range, the proposed design enables full visible spectrum transmission in a single waveguide, thereby facilitating bandwidth expansion and performance enhancement for on-chip full visible spectrum devices.
Optical image processing has the advantages of fast and parallel operation. One single-layered metasurface is designed to implement the optical imaging and edge detection of image. The dual-functional image processing is conducted without the aid of 4f system and it is switched only by the handedness of incident circularly polarized light. The designed metasurface consists of silicon nanopillars and the optimized nanopillars are equivalent to half-wave plates with the transmittance of 87%. The simulation and experimental results verify the performance of metasurface. The integrated optical metasurface enables the extremely simple image processing system and it paves the way for the applications of metasurfaces in parallel image processing and optical integrating.
High-precision detection of topological charge is significant for the practical applications of vortex beams. In view of the existing evaluation with low resolution of topological charge and more complexity to judge simultaneously integer and fraction, this paper theoretically proposes and numerically verifies the double judgment method for topological charge based on the designed metasurface. The inner and outer diffraction patterns of metasurface can judge the value and sign of topological charge. The detection precision of the proposed method reaches 0.05. The theoretic and simulated results give the solid verification for the effectiveness of the proposed method. This method has outstanding advantages including planar structure design without additional elements, direct judgment without data processing and high precision over the existing methods. We think this work is beneficial to the detection of topological charge and the applications of optical vortices.
We propose a novel fast numerical calculation method for the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction integral, which is developed based on the existing scaled convolution method. This approach enables fast calculations for general cases of off-axis scenarios where the sampling intervals and numbers of the input and observation planes are unequal. Additionally, it allows for arbitrary adjustment of the sampling interval of the impulse response function, facilitating a manual trade-off between computational load and accuracy. The errors associated with this method, which is equivalent to interpolation, primarily arise from the discontinuities of the sampling matrix of the impulse response function on its boundaries of periodic extension. To address this issue, we propose the concept of the padding function and its construction method, and we evaluate its effectiveness in enhancing computational accuracy. The feasibility of the proposed method is verified by numerical simulation and compared with the DI-method in a simplified scenario. It shows that the proposed method has good computational accuracy for the general case where the sampling interval of the input and observation plane is not equal under non-near-field diffraction, and when the diffraction distance is large, although the computational accuracy of the proposed method cannot exceed that of the DI-method, the computational amount can be significantly reduced with almost no effect on the computational accuracy. This method provides a general numerical calculation scheme of diffraction in the non-near field case for areas such as computational holography.
We designed and investigated a passive synchronized mode-locked fiber laser. The device utilizes a dual-cavity structure driven by the Nonlinear Polarization Rotation (NPR) mechanism. Stable mode-locking is attained by synergistically controlling gain, polarization state, and optical path length in two symmetric sub-cavities. Experiments proved the sub-cavity repetition frequency's tunability via the time delay line (TDL), thereby enabling synchronized mode-locking. The system stably generates multi-wavelength pulses at a single repetition frequency, evidenced by multiple spectral peaks and equidistant pulse sequences. These findings facilitate the development of high-performance multi-wavelength ultrashort pulse sources, crucial for optical communications, spectral analysis, and remote sensing.
The two-dimensional grating serves as a critical component in plane grating interferometers for achieving high-precision multidimensional displacement measurements. The calibration of grating groove density and orthogonality error of grating grooves not only improves the positioning accuracy of grating interferometers but also provides essential feedback for optimizing two-dimensional grating fabrication. This study proposes a method for simultaneous calibration of these parameters using orthogonal heterodyne laser interferometry. A two-dimensional grating interferometer is built with the grating to be measured, and a biaxial laser interferometer provides a displacement reference for it. The phase mapping relationship between grating interference and laser interference is established. The interference phase information obtained by any two displacements can simultaneously solve the above three parameters and obtain the grating installation error. The feasibility of the proposed method is verified by using a 1200 gr/mm two-dimensional grating. The standard deviation of the grating groove density in the X and Y directions is 0.012 gr/mm and 0.014 gr/mm, respectively. The standard deviation of the orthogonality error of grating grooves is 0.004°, and the standard deviation of the installation error is 0.002°. Compared with the atomic force microscope method, the consistency of the grating groove density in the X and Y directions is better than 0.03 gr/mm and 0.06 gr/mm, and the orthogonality error of grating grooves is better than 0.008°. The experimental results show that the proposed method can be simply and efficiently applied to the calibration of the grating line parameters of the two-dimensional grating.
Addressing the critical challenge of thermal radiation noise suppression in infrared systems for long-range dim target detection, this paper presents a composite detection system with an optimized cooling-based thermal radiation suppression scheme. A common-aperture optical configuration capable of simultaneous long-wave infrared and laser dual-band detection is achieved through a Ritchey-Chrétien (R-C) optical structure and a dichroic-secondary mirror with a hollow design. To mitigate thermal radiation noise, the thermal emission characteristics within the temperature range of 230 K to 320 K were analyzed using Planck’s law and non-sequential ray tracing. An improved detection range model incorporating noise terms was developed. The cooling strategy was optimized via dynamic programming, leading to an optimal solution where the main mirror and folding mirror baffles are cooled to 220 K. Experimental results demonstrate that the detection range at 300 K ambient temperature increases from 300 km to 430 km, and remains above 400 km across the entire 230−320 K range. The proposed dual-band composite detection scheme and zoned cooling methodology provide a valuable reference for the design of cold optical systems and long-range weak target detection.
This study investigates the reduction in polarization measurement accuracy caused by varying incident angles in a liquid crystal variable retarder (LCVR). The phase delay characteristics of the LCVR were examined, with particular emphasis on the influence of different two-dimensional incident angles on phase delay behavior. Building upon the calibration of phase delay under normal incidence, a phase delay calibration model was developed to account for variations in incident angle and driving voltage. A mathematical relationship was established between phase delay and the azimuth angle (
To address the challenges of complex metallic film coating processes and low integration in single-parameter detection for existing photonic crystal fiber surface plasmon resonance (PCF-SPR) sensors, a dual-parameter sensor based on gold nanowire-integrated bias-core PCF-SPR is proposed. Unlike conventional in-hole coatings or metallic film structures, the gold nanowires are directly attached to the fiber cladding via chemical vapor deposition (CVD), eliminating uneven coating issues and significantly simplifying fabrication. By optimizing the asymmetric bias-core fiber structure and leveraging the strong localized field enhancement of gold nanowires, the sensor achieves high-sensitivity synchronous detection of temperature (25−60 °C) and refractive index (1.31−1.40) in dual-polarization modes. The simulation results demonstrate that the x-polarization mode can achieve 1.31−1.40 refractive index detection with maximum wavelength sensitivity and amplitude sensitivity of
AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet (DUV) laser diodes (LDs) face performance challenges due to electron leakage and poor hole injection, often worsened by polarization effects from conventional electron blocking layers (EBLs). To overcome these limitations, we propose an EBL-free DUV LD design incorporating a 1-nm undoped Al0.8Ga0.2N thin strip layer after the last quantum barrier. Using PICS3D simulations, we evaluate the optical and electrical characteristics. Results show a significant increase in effective electron barrier height (from 158.2 meV to 420.7 meV) and a reduction in hole barrier height (from 149.2 meV to 62.8 meV), which enhance carrier injection and reduce leakage. The optimized structure (LD3) achieves a 14% increase in output power, improved slope efficiency (1.85 W/A), and lower threshold current. This design also reduces the quantum confined Stark effect and forms dual hole accumulation regions, improving recombination efficiency. Our findings present a promising approach for high-performance, EBL-free DUV LDs suitable for high-power applications.
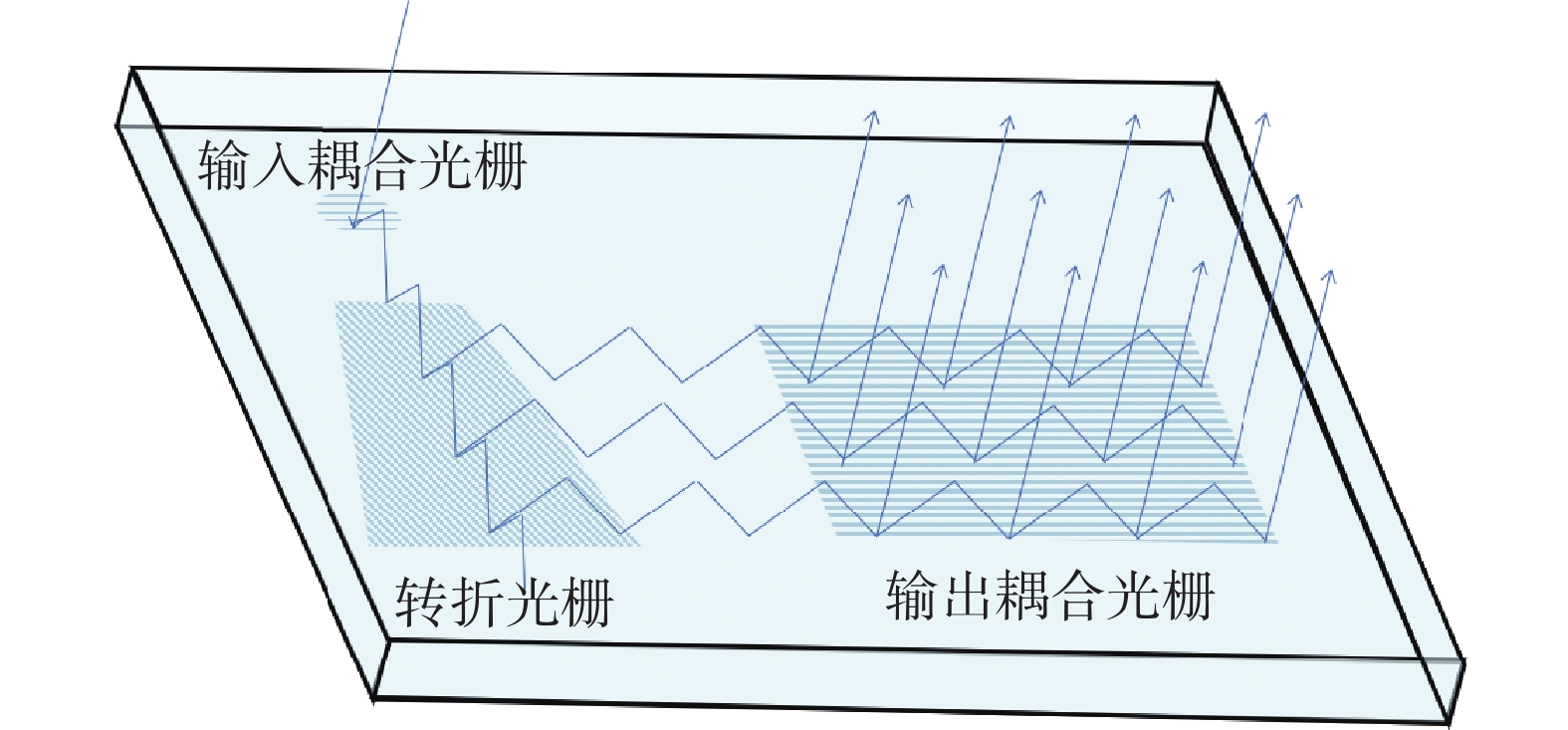
Diffractive waveguides have emerged as a particularly promising solution for augmented reality (AR) near-eye display technologies. These waveguides are characterized by their light weight, wide field of view, and large eyebox. However, most commercially available AR waveguide simulation software has been developed by foreign companies, and there has been little advancement in domestic 3D visualization software for optical waveguide design and simulation. The present study is, to the best of our knowledge, the first to develop 3D visualization module for optical waveguide design and simulation based on ray-field tracing. Using this module, a two-dimensional exit-pupil-expansion diffractive waveguide has been designed, and a systematic design workflow is demonstrated. The workflow integrates
彩色编码条纹图案已成为实现条纹投影轮廓术实时三维形貌测量的重要方法。然而,彩色相机中的色彩串扰现象仍然是限制测量精度的主要因素。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种精确的色彩串扰系数标定方法,以实现有效的色彩串扰校正。首先,设计了一种基于正交相位条纹的串扰系数估计器,从理论上推到了色彩串扰系数与相位误差的关系。同时,将设计的彩色正交条纹图案投影至标准平面靶标,实现R、G、B的彩色通道分离图案。最后,基于粒子群优化算法拟合通道串扰相位误差,从而实现高精度色彩串扰系数标定。基于标准双球球板的测量实验验证,两个球体的直径拟合误差分别为0.0191mm和0.0160mm,球心间距的计算误差低至0.0120mm,证明该方法能够有效提高彩色相机在条纹投影技术中的测量精度和适用性。


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 4960KB
PDF 4960KB